1、简单参数
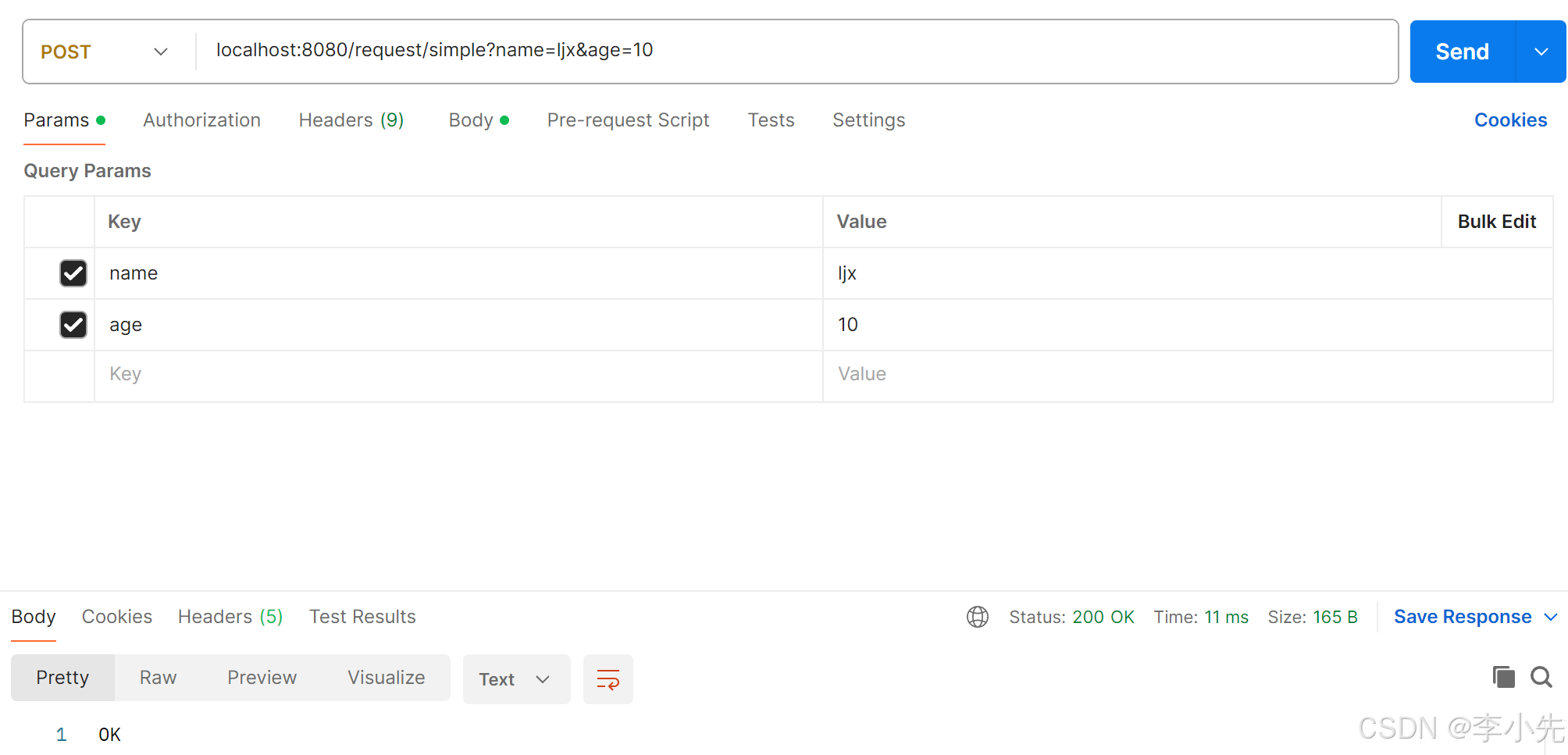
1、参数名与形参变量名相同,定义形参即可接收参数,且会自动进行类型转换。
@RequestMapping("/simple")
public String simpleParam(String name,int age){
String username = name;
int userAge = age;
System.out.println(username+"========"+userAge);
return "OK";
}
postman请求:
2、参数名与形参变量名不同,用requestParam
@RequestMapping("/simple2")
public String simpleParam2(@RequestParam(value = "name",required = false) String s_name, @RequestParam(name = "age") int s_age){
String username = s_name;
int userAge = s_age;
System.out.println(username+"========"+userAge);
return "OK";
}
postman请求:
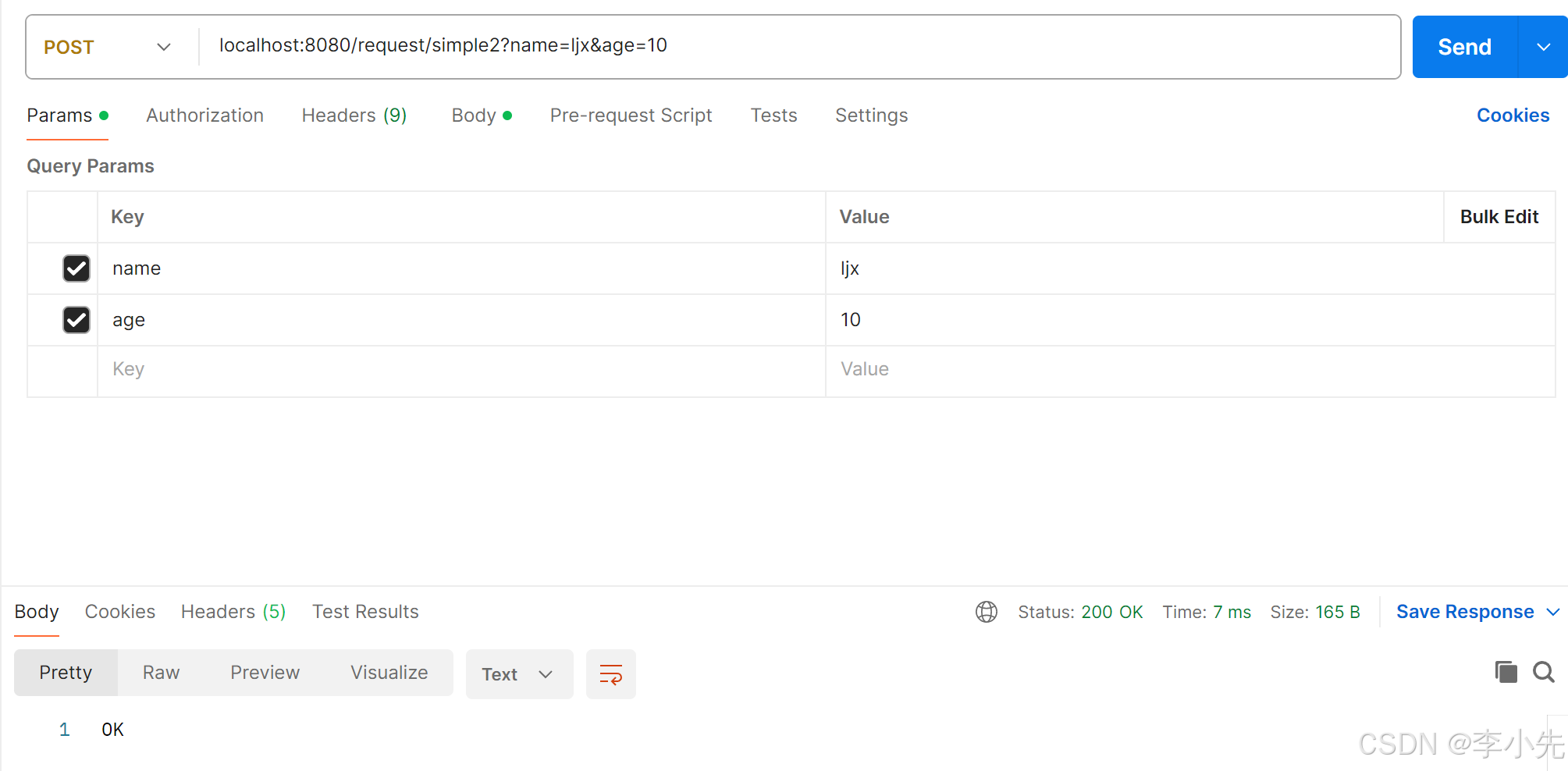
注意:@RequestParam的required默认为true,也就是说用@RequestParam指定的参数是必传项,否则报错。
2、实体参数
1、简单实体对象
请求参数名与形参对象属性名相同,定义POJO接收即可
public class User {
String name;
int age;
//省略get和set方法,toString()
}
@RequestMapping("/simplePojo")
public String simplePojo(User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "OK";
}
postman请求:

2、复杂实体对象
public class User {
String name;
int age;
Address address;
}
public class Address {
String province;
String city;
}
@RequestMapping("/complexPojo")
public String complexPojo(User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "OK";
}
postman请求:

3、数组参数
请求参数名与形参数组名称相同且请求参数为多个,定义数组类型形参即可接收参数
@RequestMapping("/arrayParam")
public String arrayParam(String[] hobby){
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hobby));
return "OK";
}
postman请求:

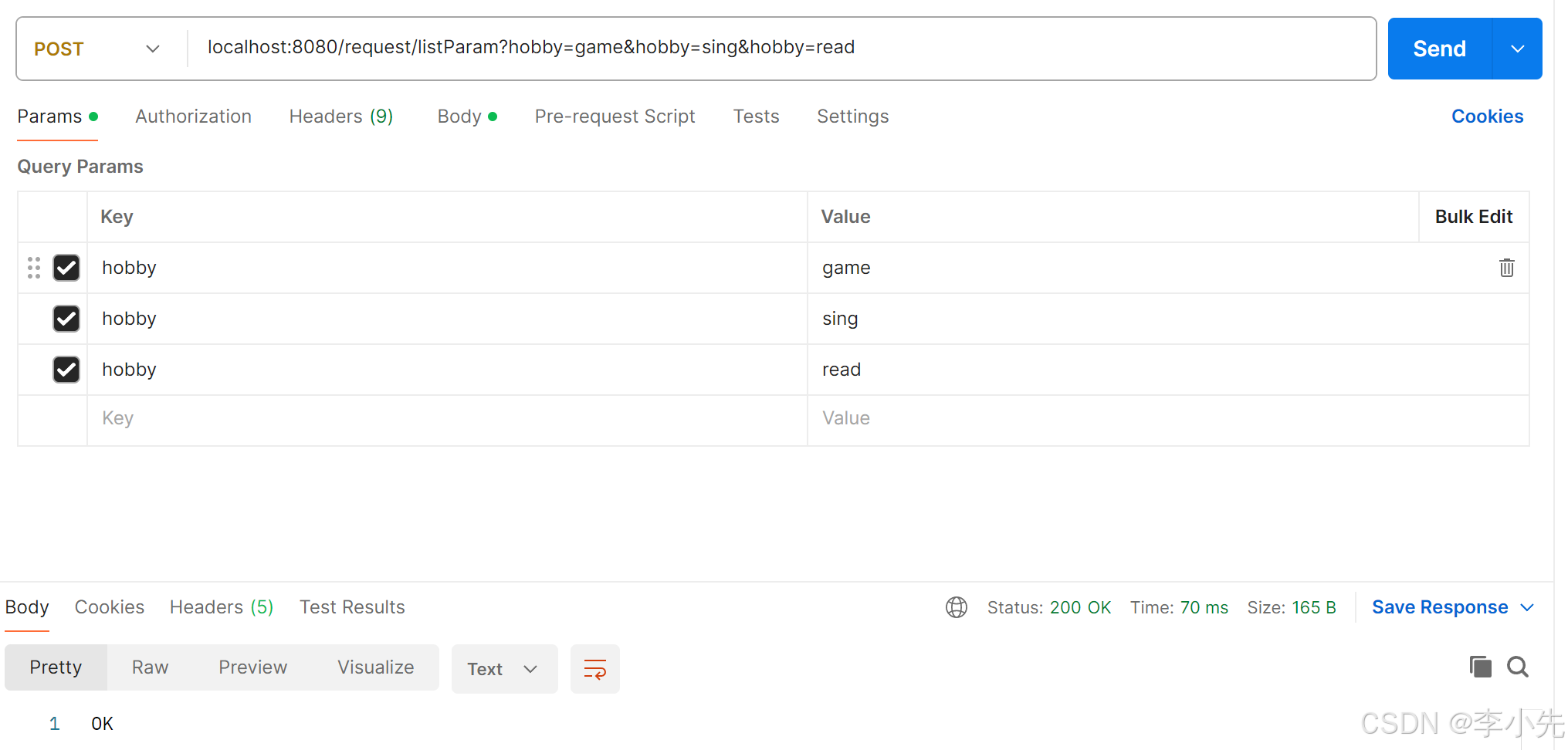
4、集合参数
请求参数名与形参集合名称相同且请求参数为多个,@RequestParam绑定参数关系
@RequestMapping("/listParam")
public String listParam(@RequestParam List hobby){
System.out.println(hobby);
return "OK";
}
postman请求:
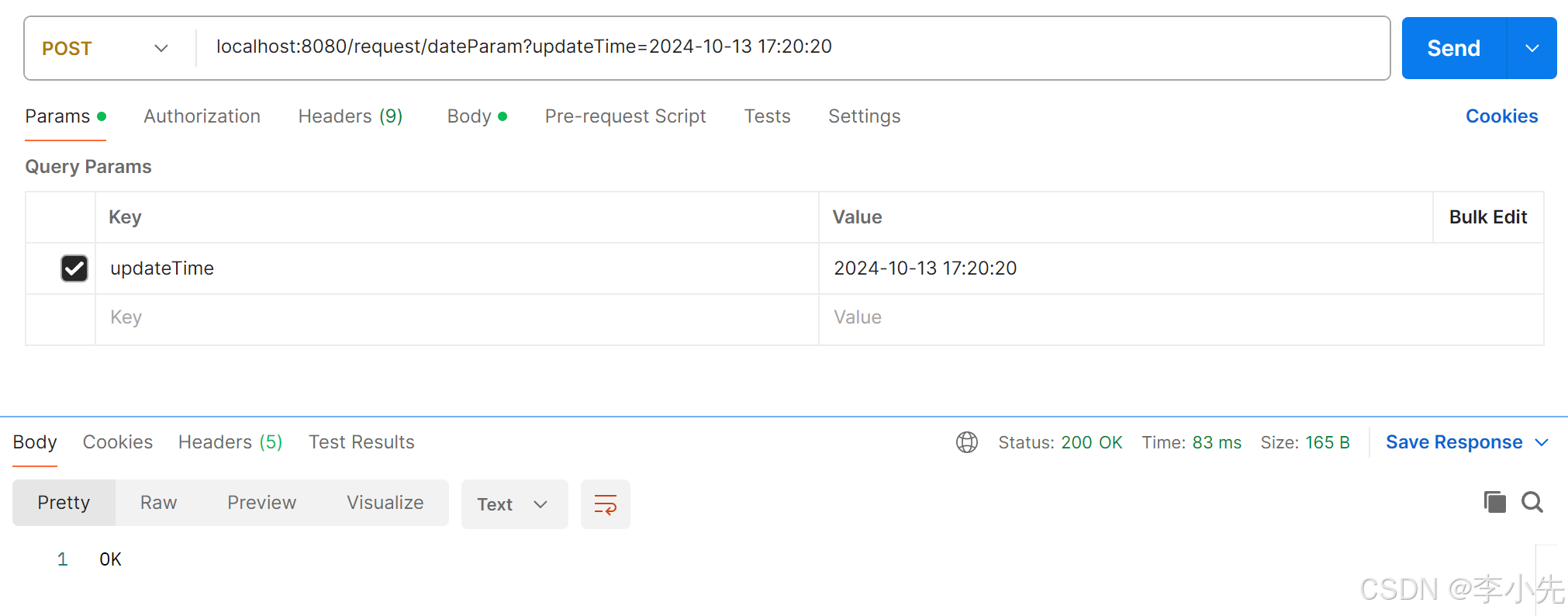
5、日期参数
使用@DateTimeFormat注解完成日期参数格式转换
@RequestMapping("/dateParam")
public String dateParam(@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") LocalDateTime updateTime){
System.out.println(updateTime);
return "OK";
}
postman请求:
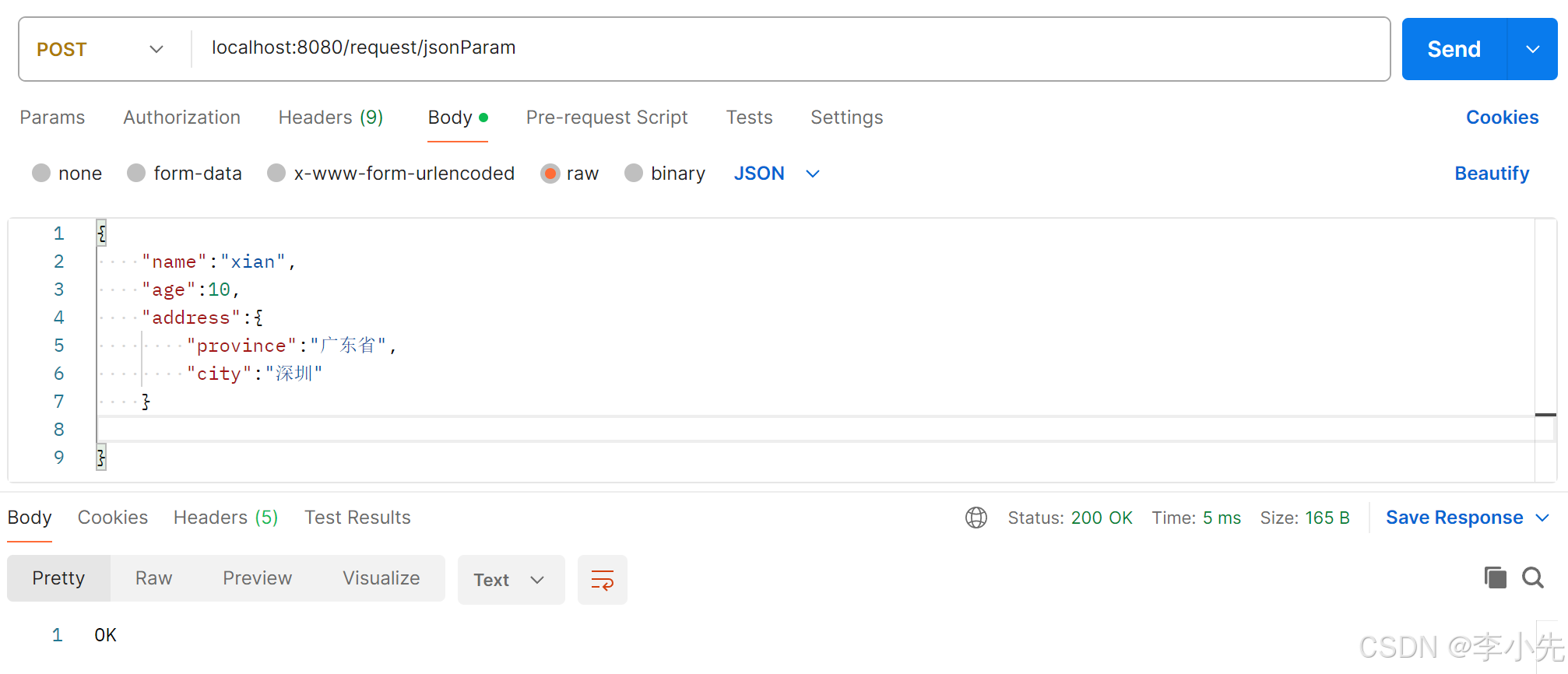
6、JSON参数
JSON数据键名与形参对象属性名相同,定义POJO类型形参即可接收参数,需要使用@RequestBody标识
@RequestMapping("/jsonParam")
public String jsonParam(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "OK";
}
postman请求:
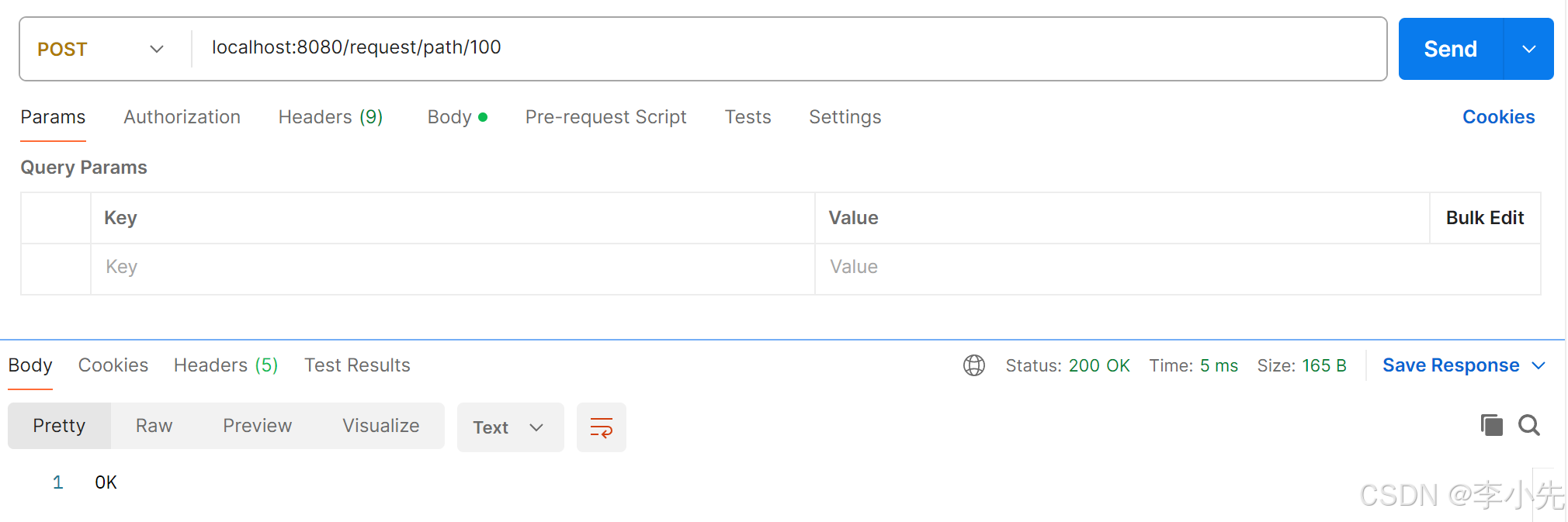
7、路径参数
通过请求URL直接传递参数,使用 {……}来标识该路径参数,需要使用@PathVariable获取路径参数
@RequestMapping("/path/{id}")
public String pathParam(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id){
System.out.println(id);
return "OK";
}
postman请求:
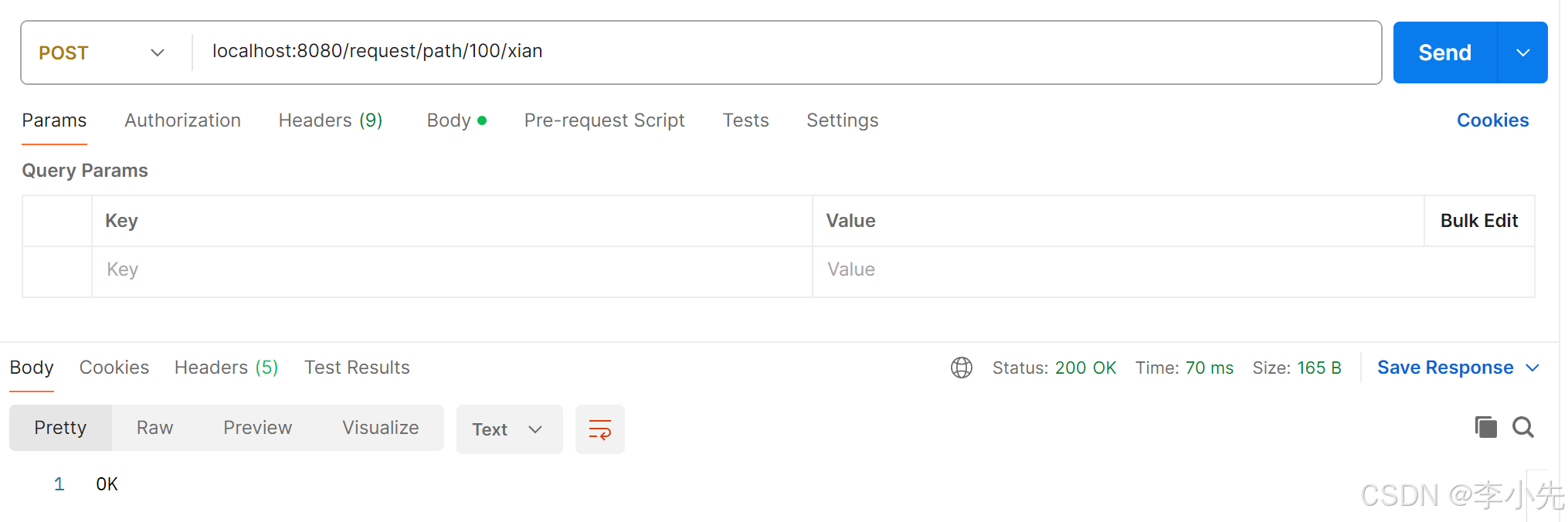
多个路径参数:
@RequestMapping("/path/{id}/{name}")
public String pathParam(@PathVariable(value = "id") Integer id,@PathVariable String name){
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(name);
return "OK";
}
postman请求:
到此这篇关于@RequestMapping对不同参数的接收方式的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关@RequestMapping参数的接收方式内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

