前言
在Java中,由于基本类型不是继承⾃Object,为了在泛型中可以⽀持基本类型,Java给每个基本类型都对应了⼀个包装类型,有些情况下只有接收泛型才可以完成其功能
包装类
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类 |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
这里的除了int 和char 类型的包装类是Integer和Character 其他的都是其首字母大写
装箱和拆箱
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
//装箱操作 将a的值放入包装类型中
Integer a1 = Integer.valueOf(a);
Integer a2 = new Integer(a);
//拆箱,将其包装类型的数据放入基本数据类型中
int i = a1.intValue();
int j = a2.intValue();
System.out.println(a1);
System.out.println(a2);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(j);
}
}
运行结果如下

上面我们在装箱和拆箱的时候,都要利用其官方的方法,这样导致代码量增多
自动装箱和拆箱
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
Integer a1 = (Integer) a;//强制类型转换
Integer a2 = a;//自动类型转换
int a3 = a1;//自动类型转换
int a4 = (int) a2;//强制类型转换
System.out.println(a1);
System.out.println(a2);
System.out.println(a3);
System.out.println(a4);
}
}
这里可以强制类型转换,也可以自动类型转换,Java是提供了这个机制
运行结果如下

基本类型和包装类型其实并不完全相同
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a1 = 10;
Integer a2 = 10;
Integer a3 = 128;
Integer a4 = 128;
System.out.println(a1==a2);
System.out.println(a3==a4);
}
}
运行结果如下

这里是自动调用其Integer.valueOf方法
这里如果换成普通数据类型这里就相同了,就输出两个true,但是换成包装类型,这里的结果就变了,为什么呢,这就要看看其包装类型的存储了

因为这里的传入值如果为[-128,127]放其给定好的数组中,反之则new一个新对象,所以这里超过其这个范围两个地址不相同了,所以这里的127返回true,128返回false
泛型
泛型的概念
以前在写方法的时候,都是使用的基本类型,这样此方法只可以用于这一种类型,那可不可以创建一个方法可以让多种数据类型都可以使用呢,这就引入了泛型,就是其可以使用多种类型
我们可以先自己定义一个数组可以存放多种类型的数据,里面有存放和获取一个下标数值
class MyArray{
public Object[] array = new Object[10];
public Object getval(int index){
return array[index];
}
public void setval(int index,int val){
this.array[index] = val;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArray myArray = new MyArray();
myArray.setval(0,1);
System.out.println(myArray.getval(0));
}
}
运行结果如下

但是要注意创建一个对象以后,添加了一种类型的数据,就不可以在添加另外一种数据了
一个数组中的元素类型要一致
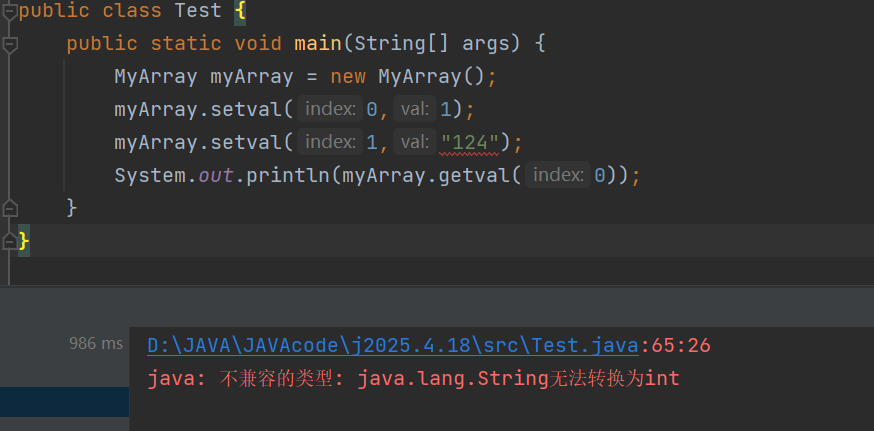
就像上面已经添加了int类型就说明这里是int类型数组,因此不可以在添加其他数据类型,这里如果在添加String类型就会出错
泛型的使用
定义一个泛型类
class 泛型类名称 {
} // 这⾥可以使⽤类型参数
也可以放多种类型
class ClassName {
}
这个泛型方法的使用
泛型类 变量名= new 泛型类(构造⽅法实参);
//定义一个泛型类引用,并实例化一个对象
例如
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();//实例化一个Integer数据类型的列表
这里在实例化的时候内不用在写是什么类型,编译器会从前面推导出来
有了这个上面的代码就可以改为
class MyArray{
public Object[] array = new Object[10];
public T getval(int index){
return (T)array[index];
}
public void setval(int index,int val){
this.array[index] = val;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//这里指定了是Integer包装类型的数组
//就不可以存储其以外的数据了
MyArray myArray = new MyArray();
myArray.setval(0,1);
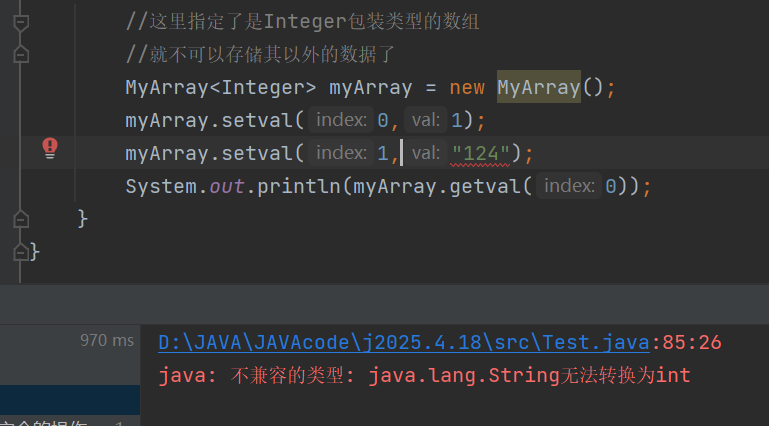
//myArray.setval(1,"124");
System.out.println(myArray.getval(0));
}
}
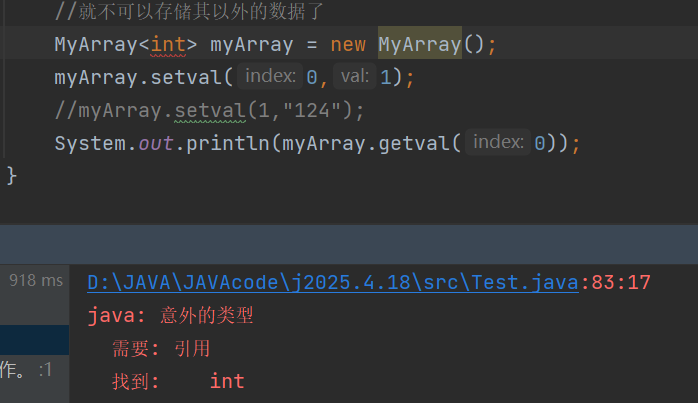
这里在创建对象的时候就确定了是什么数据类型的数组
并且这里的数组数据类型只可以是包装类型
1.如果写成普通数据类型就会报错,这里需要的是包装类型
2.确定了数据类型就不可以存放其他数据类型了
交换的泛型方法
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] arr ={1,2,3};
swap(arr,1,2);
}
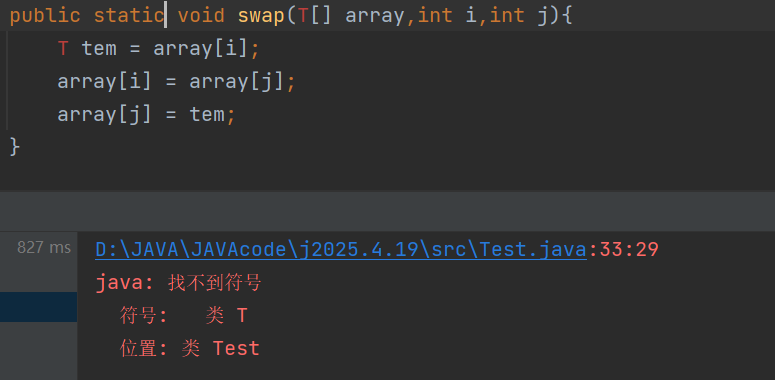
//这里静态泛型方法前面要说明是什么类型
public static void swap(T[] array,int i,int j){
T tem = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = tem;
}
}
这里前面的T是不可以省略的,用于确定其是什么类型
1.类名后的 代表占位符,表⽰当前类是⼀个泛型类 E表⽰Element, K表⽰Key , V表⽰Value ,N表⽰Number ,T表⽰Type 2.创建对象的时候就确认其数组数据类型,并且只可以是包装类型 3.确认数据类型就不可以在其数组放入其他数据类型的数据了
泛型的上界
在定义泛型类的时候有时候我们要对其传入数据类型进行限制,于是就引出了泛型的上界
class 泛型类名称 {
…
}
例如上面
public class MyArray {
…
}
//这里表示上界是Number
例如
class MyArray{
public Object[] array = new Object[10];
public T getval(int index){
return (T)array[index];
}
public void setval(int index,int val){
this.array[index] = val;
}
}
例如上面这个类就是上界是Number
也就是这里是要是int double float类型等等数字类型
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArray myArray = new MyArray();
MyArray myArray1 = new MyArray();
MyArray myArray2 = new MyArray();
}
}
这里要求的上界是Number数字,如果不是数字类型的包装类型就会报错,例如下面传入引用数据类型就会报错
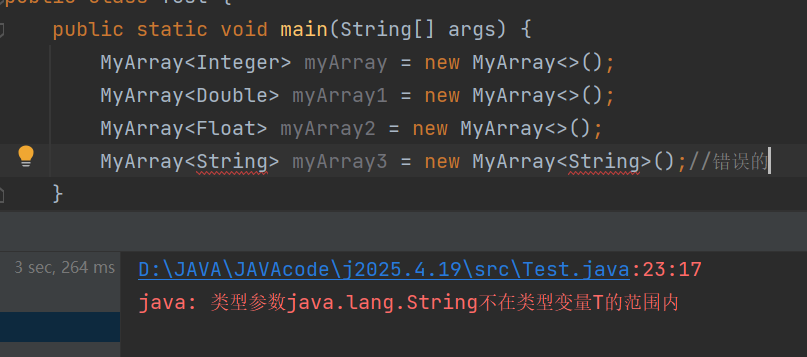
通配符
通配符概念
?也可以用于泛型的使用,也就是通配符
class Message{
private T message;
public T getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(T message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Message message = new Message();
message.setMessage("hello world");
fun(message);
}
public static void fun(Message message){
System.out.println(message.getMessage());
}
}
运行结果如下

我们发现上面的fun函数并不是泛型,只可以打印和接收String类型,如果是其他的类型就会报错,这明显不符合我们的需求,我们要其可以接收和打印多种类型
如果这里传入Integer类型就会报错
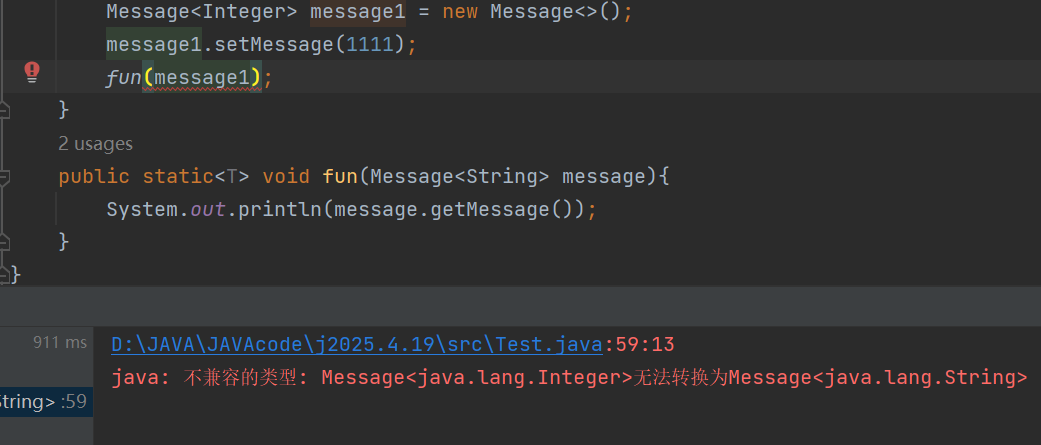
因此这时候我们就可以使用通配符?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Message message = new Message();
message.setMessage("hello world");
fun(message);
Message message1 = new Message();
message1.setMessage(1111);
fun(message1);
}
//传入什么类型,这个就是什么类型
public static void fun(Message> message){
System.out.println(message.getMessage());
}
}
运行结果如下

其实这里我们使用上面的泛型也可以
public static void fun(Message message){
System.out.println(message.getMessage());
}
通配符上界
定义了一个Food类
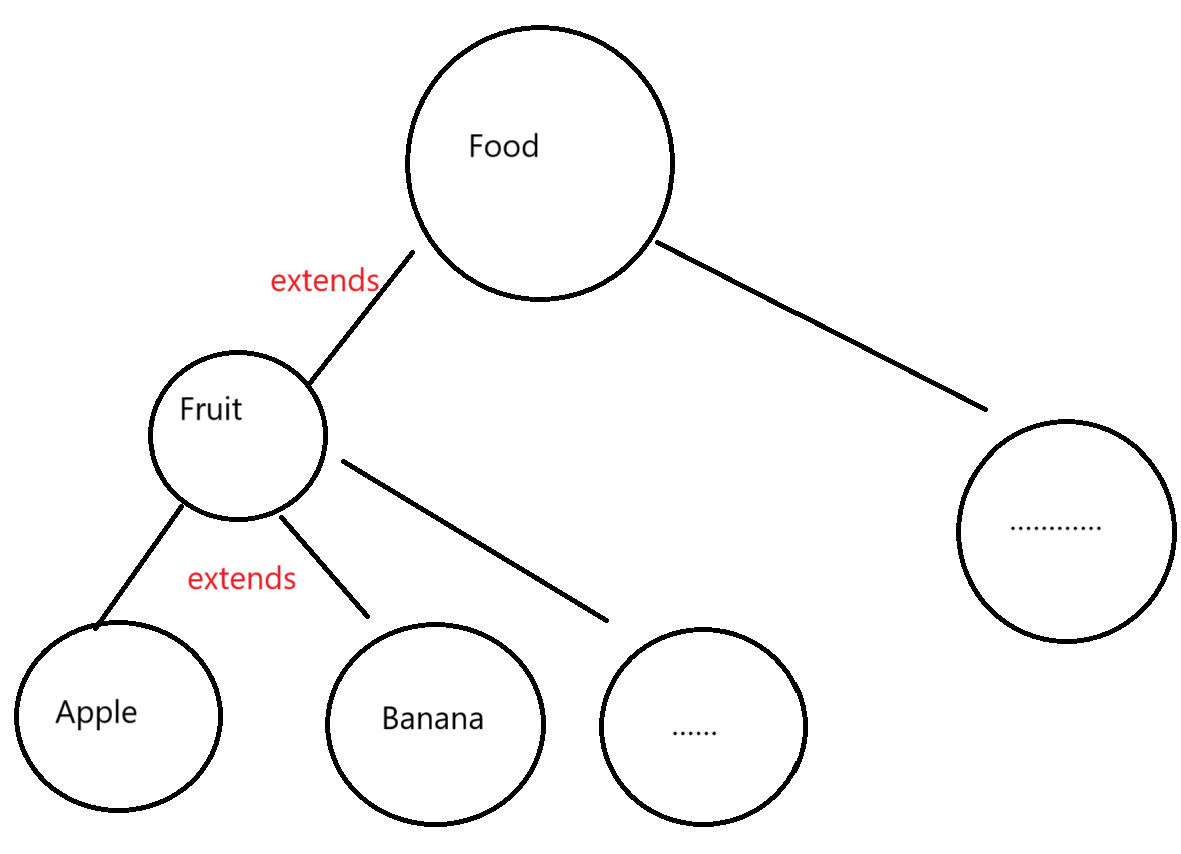
class Food{
}
class Fruit extends Food{
}
class Banana extends Fruit{
}
class Apple extends Fruit{
}
class Plate{
private T plate;
public T getPlate() {
return plate;
}
public void setPlate(T plate) {
this.plate = plate;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//这里的类型要为Fruit或者其子类
Plate plate1 = new Plate();
plate1.setPlate(new Apple());
fun(plate1);
Plate plate2 = new Plate();
plate2.setPlate(new Banana());
fun(plate2);
// fun(new Food());//这个超越了上界
}
//fun用于打印
//这里表示只可以传入Fruit及其子类
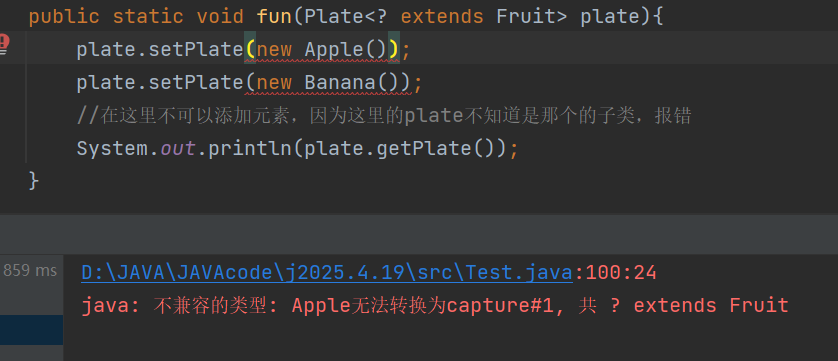
public static void fun(Plate extends Fruit> plate){
// plate.setPlate(new Apple());
// plate.setPlate(new Banana());
//在这里不可以添加元素,因为这里的plate不知道是那个的子类,报错
System.out.println(plate.getPlate());
}
}
运行结果如下
这里的fun函数参数的上界为Fruit,所以其只可以接收,Fruit及其子类
如果传入Food,是Fruit的父类肯定报错,超越了上界
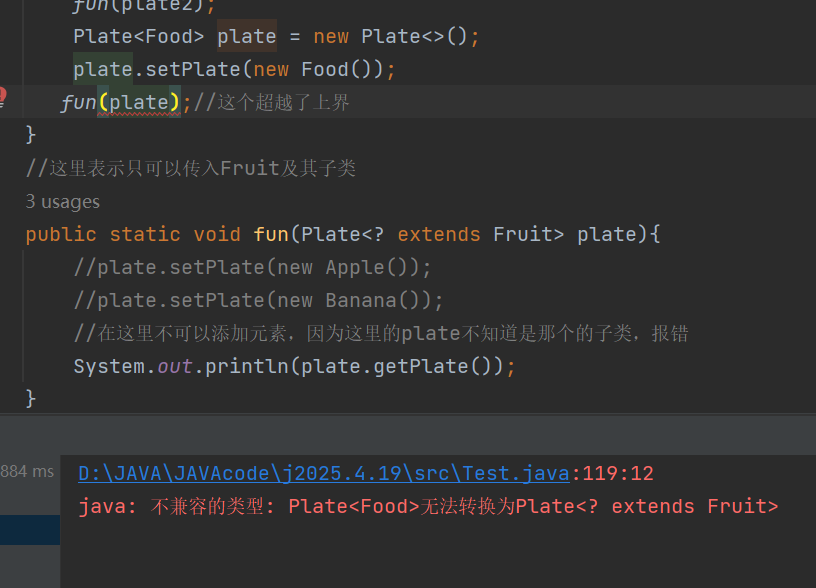
并且不可以在其fun函数里,来进行添加元素
因为这里的plate是那个子类我们并不知道,不知道添加什么类型的元素
通配符下界
super 下界>
还是利用上面的
class Food{
}
class Fruit extends Food{
}
class Banana extends Fruit{
}
class Apple extends Fruit{
}
class Plate{
private T plate;
public T getPlate() {
return plate;
}
public void setPlate(T plate) {
this.plate = plate;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Plate plate = new Plate();
plate.setPlate(new Fruit());
fun(plate);
Plate plate1 = new Plate();
plate1.setPlate(new Food());
fun(plate1);
// Plate plate2 = new Plate();
// plate2.setPlate(new Apple());
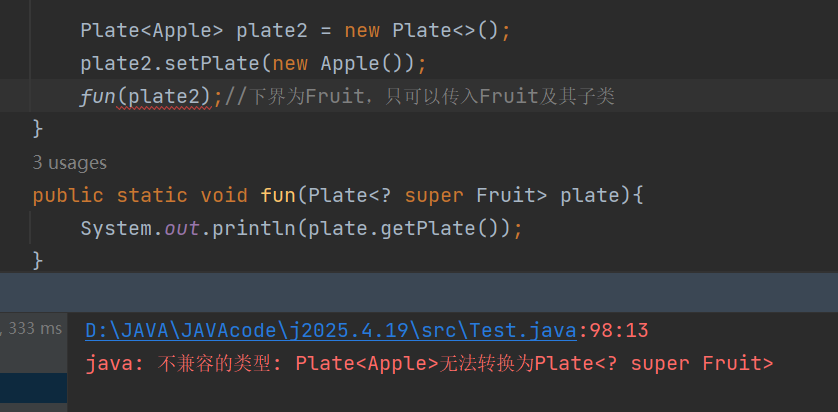
// fun(plate2);//下界为Fruit,只可以传入Fruit及其子类
}
public static void fun(Plate super Fruit> plate){
System.out.println(plate.getPlate());
}
}
运行结果如下

这里下界为Fruit,只可以传入Fruit及其父类
不可以传入其子类
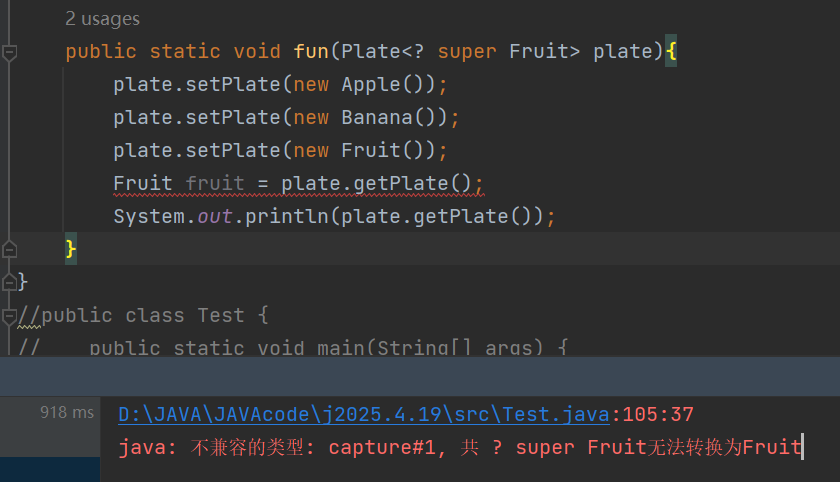
由于这里fun函数接收的下界为Fruit,所以其是可以在里面添加其Fruit子类对象
public static void fun(Plate super Fruit> plate){
plate.setPlate(new Apple());
plate.setPlate(new Banana());
plate.setPlate(new Fruit());
System.out.println(plate.getPlate());
}
虽然可以添加,但是不可以接收,因为不知道是用哪一个父类来接收,Fruit可能有很多父类
到这里就结束了。
以上就是一文详解Java中的包装类和泛型的详细内容,更多关于Java包装类和泛型的资料请关注IT俱乐部其它相关文章!

