1.传递引用
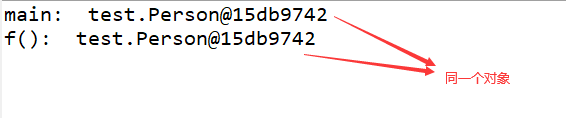
在一个方法中将一个对象的引用传递给另外一个方法,引用指向的对象是同一个
public class Person {
int age;
String name;
public Person(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p=new Person(18, "tom");
System.out.println("main: "+p);
f(p);
}
public static void f(Person p) {
System.out.println("f(): "+p);
}
}
引用别名
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p=new Person(18, "tom");
Person p2=p;
p2.age++;
System.out.println(p.age);//19
}
引用p和p2指向的是同一个对象,p2对对象的属性进行操作,当使用引用p访问对象的属性时当然也改变,同样的情况也发生在对象引用在方法之间的传递,如下面的代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p=new Person(18, "tom");
f(p);
System.out.println(p.age);//19
}
public static void f(Person p) {
p.age++;
}
2. 创建本地副本
几个概念:
- 引用别名会在方法参数是对象类型时自动发生
- 没有本地对象,只有本地引用(方法中创建的对象存在于堆中,只有引用变量存在于方法栈中)
- 引用是有作用域的,而对象没有
- Java中的对象的生命周期并不是一个问题(垃圾回收机制)
2.1 值传递
Java中方法之间只有值传递
传递基本类型时,传递的是基本类型的值的拷贝
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=100;
change(a);
System.out.println(a);//100 不受影响
}
public static void change(int a) {
a=99;
}
传递对象时,传递的是对象的引用拷贝
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p=new Person(18, "tom");
f(p);
System.out.println(p.age);//还是18 f()中p指向了一个新的对象 不影响main函数
}
public static void f(Person p) {
p=new Person(20, "bob");
}
传递对象时如果在另外一个方法中对对象的属性进行操作会对main方法产生“副作用”, 但是如果只是简单的对引用进行操作是没有影响的
2.2 对象克隆
步骤:
类实现Cloneable空接口,默认情况下不希望所有的类都有克隆能力,当需要某个类有克隆能力时就需要实现该接口作为一种“可克隆”的标记,否则克隆时会报错CloneNotSupportedException
public interface Cloneable {
}
重写clone方法,clone方法是Object类中的,它在Object类中的是一个protected的本地方法,需要重写,加上public修饰符,否则只能在当前类中使用clone方法
protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
public class Person implements Cloneable {
int age;
String name;
public Person(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
public Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Person) super.clone();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person p1=new Person(18, "tom");
Person p2=p1.clone();
System.out.println(p1+" name: "+p1.name+" age: "+p1.age);
System.out.println(p2+" name: "+p2.name+" age: "+p2.age);
}
}

重写clone方法时实际是就是调用Object类中的本地clone方法,Object类中的clone方法做了哪些工作?
Object类中clone方法负责创建正确大小的存储空间,并执行了从原始对象中所有二进制位到新对象内存中的按位复制。
2.3 浅拷贝问题
场景:Person类中增加一个引用类型的属性Country, 表示这个人所属的国家,然后进行克隆
package test;
class Country{
String nation;
public Country(String nation) {
super();
this.nation = nation;
}
}
public class Person implements Cloneable {
int age;
String name;
Country country;
public Person(int age, String name,Country country) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.country=country;
}
public Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Person) super.clone();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Country country=new Country("China");
Person p1=new Person(18, "tom",country);
Person p2=p1.clone();
System.out.println(p1+" name: "+p1.name+" age: "+p1.age+" country: "+p1.country);
System.out.println(p2+" name: "+p2.name+" age: "+p2.age+" country: "+p2.country);
p1.name="bob";
p1.country.nation="America";
System.out.println(p1+" name: "+p1.name+" age: "+p1.age+" country: "+p1.country.nation);
System.out.println(p2+" name: "+p2.name+" age: "+p2.age+" country: "+p2.country.nation);
}
}
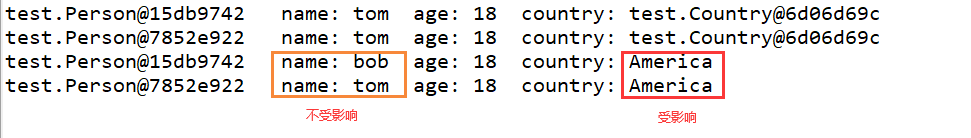
问题描述: 当Person类中有一个引用类型属性时,对于基本类型数据和String类型是对值进行拷贝的,因此改变p1的name不影响p2的name, 但是对于Country这种引用类型,在clone时仅仅是拷贝了一份对象的引用,拷贝的引用和原来的引用指向的是同一个对象,因此p1改变country的属性时,p2的country的属性也发生了改变
2.4 深拷贝
解决浅拷贝问题的关键点在于不仅仅是拷贝引用,而且要拷贝一份引用指向的对象,深拷贝有两种方式:
- 逐个对引用指向的对象进行浅拷贝
- 使用序列化方式进行深拷贝
2.4.1 引用类型逐个浅拷贝
如果一个类A中有多个引用类型,那么这些引用类型的类需要实现 Cloneable接口,在对A的对象进行克隆时,逐个浅拷贝其中的引用类型
eg: Person类中有Country引用类型,在进行clone时,单独对country进行浅拷贝
package test;
class Country implements Cloneable{
String nation;
public Country(String nation) {
super();
this.nation = nation;
}
public Country clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
return (Country) super.clone();
}
}
public class Person implements Cloneable {
int age;
String name;
Country country;
public Person(int age, String name,Country country) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.country=country;
}
public Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person p=null;
p=(Person) super.clone();
p.country=p.country.clone();//对country进行浅拷贝
return p;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Country country=new Country("China");
Person p1=new Person(18, "tom",country);
Person p2=p1.clone();
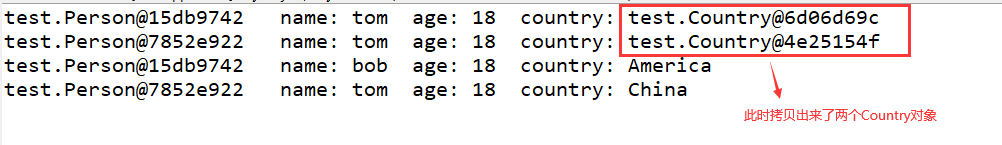
System.out.println(p1+" name: "+p1.name+" age: "+p1.age+" country: "+p1.country);
System.out.println(p2+" name: "+p2.name+" age: "+p2.age+" country: "+p2.country);
p1.name="bob";
p1.country.nation="America";
System.out.println(p1+" name: "+p1.name+" age: "+p1.age+" country: "+p1.country.nation);
System.out.println(p2+" name: "+p2.name+" age: "+p2.age+" country: "+p2.country.nation);
}
}
2.4.2 序列化方式进行深拷贝
package test;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
class Country implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
String nation;
public Country(String nation) {
super();
this.nation = nation;
}
}
public class Person implements Cloneable,Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
int age;
String name;
Country country;
public Person(int age, String name,Country country) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.country=country;
}
public Person clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Person p=null;
ObjectInputStream ois=null;
ObjectOutputStream oos=null;
ByteArrayInputStream bais=null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos=null;
try {
baos=new ByteArrayOutputStream();
oos=new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeObject(this);//Person对象序列化 序列化写入到baos流中
bais=new ByteArrayInputStream(baos.toByteArray());
ois=new ObjectInputStream(bais);//从baos流中读取数据到ois
p=(Person) ois.readObject();//ois读取对象数据
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(bais!=null)
try {
bais.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(baos!=null)
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(oos!=null)
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if(ois!=null)
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return p;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {
Country country=new Country("China");
Person p1=new Person(18, "tom",country);
Person p2=p1.clone();
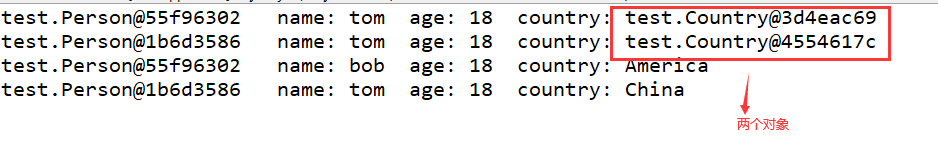
System.out.println(p1+" name: "+p1.name+" age: "+p1.age+" country: "+p1.country);
System.out.println(p2+" name: "+p2.name+" age: "+p2.age+" country: "+p2.country);
p1.name="bob";
p1.country.nation="America";
System.out.println(p1+" name: "+p1.name+" age: "+p1.age+" country: "+p1.country.nation);
System.out.println(p2+" name: "+p2.name+" age: "+p2.age+" country: "+p2.country.nation);
}
}
总结: 实现一个可克隆的类的步骤
- 实现Cloneable接口
- 重写clone方法
- 在重写的clone方法中调用super.clone()方法
- 在重写的clone方法中捕获异常
总结
到此这篇关于Java对象传递与返回细节问题的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java对象传递与返回内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

