前言
MyBatis中也提供了注解式开发⽅式,采⽤注解可以减少Sql映射⽂件的配置。 当然,使⽤注解式开发的话,sql语句是写在java程序中的,这种⽅式也会给sql语句的维护带来成本。
官⽅是这么说的:

使⽤注解编写复杂的SQL是这样的:
@Update(" update table_name set grade='三年级'”+
" , name = #{name} ”+
" , sex = #{sex}”+
" where num = #{num}")
void update(Student student);
原则:简单sql可以注解,复杂sql使⽤xml!使用注解式开发以后三兄弟之一的SqlMapper.xml文件就不需要了!
1. @Insert注解
二兄弟之一CarMapper接口,用来编写方法
使用@Insert的注解方式,在注解上就可以写上SQL语句,对于SQL语句当中的变量就是pojo类Car对应的变量名
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
public interface CarMapper {
// 使用注解式开发,插入数据
@Insert("insert into t_car values(null,#{carNum},#{brand},#{guidePrice},#{produceTime},#{carType})")
int insert(Car car);
}
二兄弟之二CarMapperTest,用来测试
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.test;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CarMapperTest {
@Test
public void testInsert(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
// 创建Car对象
Car car = new Car(null, "666", "丰田霸道", 32.0, "2023-1-9", "燃油车");
int count = mapper.insert(car);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}
执行结果:

2. @Delete注解
二兄弟之一CarMapper接口,用来编写方法
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
public interface CarMapper {
// 使用注解式开发,删除数据
@Delete("delete from t_car where id = #{id}")
int deleteById(Long id);
}
二兄弟之二CarMapperTest,用来测试
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.test;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CarMapperTest {
@Test
public void testDeleteById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
int count = mapper.deleteById(40L);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}
执行结果:
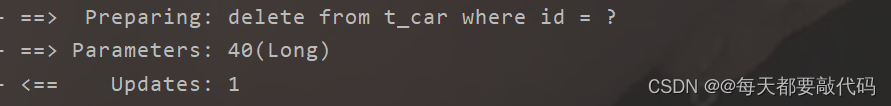
3. @Update注解
二兄弟之一CarMapper接口,用来编写方法
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
public interface CarMapper {
// 使用注解式开发,更新数据
@Update("update t_car set car_num=#{carNum},brand=#{brand},guide_price=#{guidePrice},produce_time=#{produceTime},car_type=#{carType} where id = #{id}")
int update(Car car);
}
二兄弟之二CarMapperTest,用来测试
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.test;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CarMapperTest {
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
// 创建Car对象,根据id进行更新
Car car = new Car(34L, "666", "丰田霸道", 32.0, "2023-1-9", "燃油车");
int count = mapper.update(car);
System.out.println(count);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}
执行结果:

4. @Select注解
二兄弟之一CarMapper接口,用来编写方法
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
public interface CarMapper {
// 使用注解式开发,查询数据
@Select("select * from t_car where id = #{id}")
Car selectById(Long id);
}
二兄弟之二CarMapperTest,用来测试
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.test;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper.CarMapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.utils.SqlSessionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CarMapperTest {
@Test
public void testSelectById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtil.openSession();
CarMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CarMapper.class);
Car car = mapper.selectById(41L);
System.out.println(car);
sqlSession.close();
}
}
执行结果:

5. @Results注解
我们知道数据库表中的字段和pojo类的属性名有的是不一样的,我们之所以能够完整的查出数据,是因为在核心配置文件mybatis-config.xml当中配置了:启用驼峰命名⾃动映射
如果我们不启用,不对应的字段就是null,查询的数据如下:

那还有什么办法呢?还可以使用@Results注解!
注:从这里也能看出,使用注解的方式开发,对于简单点的SQL还行,对于稍微复杂的查询语句就太麻烦了!
package com.bjpowernode.mybatis.mapper;
import com.bjpowernode.mybatis.pojo.Car;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
public interface CarMapper {
// 使用注解式开发,查询数据
@Select("select * from t_car where id = #{id}")
@Results({
@Result(property = "id",column = "id"),
@Result(property = "carNum",column = "car_num"),
@Result(property = "brand",column = "brand"),
@Result(property = "guidePrice",column = "guide_price"),
@Result(property = "produceTime",column = "produce_time"),
@Result(property = "carType",column = "car_type"),
})
Car selectById(Long id);
}
这样计算我们不启用驼峰命名⾃动映射,也能正常查询数据

结语:直到今天MyBatis的学习就完美撒花了,接下来就开始Spring的学习,敬请期待!
到此这篇关于MyBatis注解式开发映射语句详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关MyBatis注解式开发内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

