Java8中的forEach使用
forEach
Java中的forEach是一个用于迭代集合或流,且可以对迭代的每个元素进行特定操作的实用方法。
1. forEach method
下面的代码片段展示了forEach方法在Iterable接口中的默认实现,它使这个方法对除了Map之外的所有集合都可用。
该方法对迭代器的每个元素执行给定的操作,直到处理完所有元素或操作引发异常为止。
该action表示接受单个参数而不返回结果的一个操作。它是Consumer接口的一个实例。
Iterable.java
default void forEach(Consumer super T> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
for (T t : this) {
action.accept(t);
}
}
也可以使用以下这种简单语法创建自定义操作.这里把Object类型替换为collection或stream中的元素类型.
Consumer
2. Java 8 stream forEach example
用于迭代流的所有元素并执行特定操作的Java程序,这里的例子,我们打印所有的偶数
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); Consumer action = System.out::println; list.stream().filter(n -> n % 2 == 0).forEach(action);
输出为:
2
4
1
2
3. Java forEach examle using List
用于迭代arrayList中的所有元素并执行指定操作的java程序:
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); Consumer action = System.out::println; list.forEach(action);
输出:
1
2
3
4
5
4. Java forEach example using Map
用于遍历HashMap中的所有Entry实体,并执行相关操作。
我们可以迭代map中的key和value并可以对所有元素进行任何操作.
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("A", 1);
map.put("B", 2);
map.put("C", 3);
// 1.Map entries
Consumer
输出结果:
A=1
B=2
C=3
A
B
C
5. Create custom action(自定义操作)
我们也可以自定义操作方法为集合中的每个元素执行自定义逻辑。
HashMap map = new HashMap();
map.put("A", 1);
map.put("B", 2);
map.put("C", 3);
// 1.Map entries
Consumer
输出结果:
Key is A
Value is 1Key is B
Value is 2Key is C
Value is 3
Java8中foreach()不能break,如果需要continue时,怎么办
结论
在Java8的foreach()中不能break,如果需要continue时,可以使用return。
lambda表达式中使用return时,这个方法是不会返回的,而只是执行下一次遍历。
测试代码
List list = Arrays.asList("12", "14345", "16", "abch", "sdfhrthj", "mvkd");
list.stream().forEach(e ->{
if(e.length() >= 3){
return;
}
System.out.println(e);
});
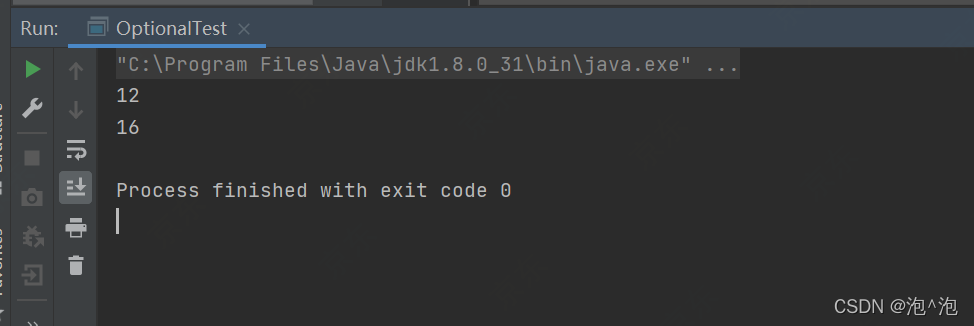
可以看出return起到的作用和continue是相同的。
原因
Stack Overflow中的答案,主要是说foreach()不是一个循环,不是设计为可以用break以及continue来中止的操作。
最后
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持IT俱乐部。

