1 数据准备
create table area_test( id number(10) not null, parent_id number(10), name varchar2(255) not null ); alter table area_test add (constraint district_pk primary key (id)); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (1, null, '中国'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (11, 1, '河南省'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (12, 1, '北京市'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (111, 11, '郑州市'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (112, 11, '平顶山市'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (113, 11, '洛阳市'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (114, 11, '新乡市'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (115, 11, '南阳市'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (121, 12, '朝阳区'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (122, 12, '昌平区'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (1111, 111, '二七区'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (1112, 111, '中原区'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (1113, 111, '新郑市'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (1114, 111, '经开区'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (1115, 111, '金水区'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (1121, 112, '湛河区'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (1122, 112, '舞钢市'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (1123, 112, '宝丰市'); insert into area_test (ID, PARENT_ID, NAME) values (11221, 1122, '尚店镇');
2 start with connect by prior递归查询
2.1 查询所有子节点
select * from area_test start with name ='郑州市' connect by prior id=parent_id
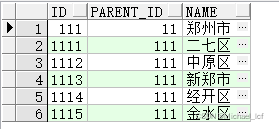
2.2 查询所有父节点
select t.*,level from area_test t start with name ='郑州市' connect by prior t.parent_id=t.id order by level asc;
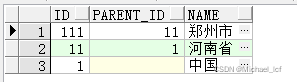
start with 子句:遍历起始条件,如果要查父结点,这里可以用子结点的列,反之亦然。
connect by 子句:连接条件。prior 跟父节点列parentid放在一起,就是往父结点方向遍历;prior 跟子结点列subid放在一起,则往叶子结点方向遍历。parent_id、id两列谁放在“=”前都无所谓,关键是prior跟谁在一起。
order by 子句:排序。
2.3 查询指定节点的,根节点
select d.*, connect_by_root(d.id) rootid, connect_by_root(d.name) rootname from area_test d where name='二七区' start with d.parent_id IS NULL connect by prior d.id=d.parent_id
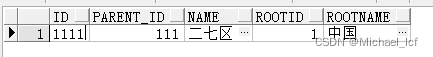
2.4 查询巴中市下行政组织递归路径
select id, parent_id, name, sys_connect_by_path(name, '->') namepath, level from area_test start with name = '平顶山市' connect by prior id = parent_id
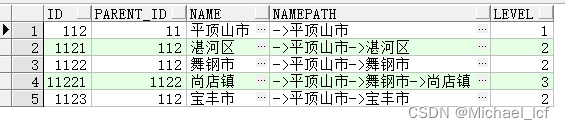
3 with递归查询
3.1 with递归子类
with tmp(id, parent_id, name)
as (
select id, parent_id, name
from area_test
where name = '平顶山市'
union all
select d.id, d.parent_id, d.name
from tmp, area_test d
where tmp.id = d.parent_id
)
select * from tmp;
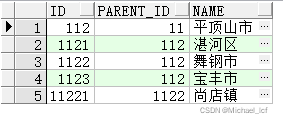
3.2 递归父类
with tmp(id, parent_id, name) as ( select id, parent_id, name from area_test where name = '二七区' union all select d.id, d.parent_id, d.name from tmp, area_test d where tmp.parent_id = d.id ) select * from tmp;
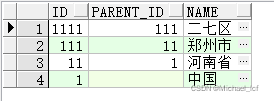
补充:实例
我们称表中的数据存在父子关系,通过列与列来关联的,这样的数据结构为树结构。
现在有一个menu表,字段有id,pid,title三个。
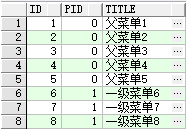
查询菜单id为10的所有子菜单。
SELECT * FROM tb_menu m START WITH m.id=10 CONNECT BY m.pid=PRIOR m.id;
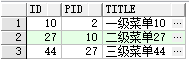
将PRIOR关键字放在m.id前面,意思就是查询pid是当前记录id的记录,如此顺延找到所有子节点。
查询菜单id为40的所有父菜单。
SELECT * FROM tb_menu m START WITH m.id=40 CONNECT BY PRIOR m.pid= m.id ORDER BY ID;
总结
到此这篇关于Oracle递归查询的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Oracle递归查询内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

