在日常工作中,我们经常会遇到需要处理多个Excel工作表(Sheet)的情况。比如,一个Excel文件中包含了一个月内每天的数据,每个工作表代表一天。有时候,为了方便分析,我们需要将这些分散的数据合并到一个工作表中。手动复制粘贴不仅效率低下,而且容易出错。这时,我们可以使用Python的pandas库和openpyxl库来自动化这个过程。
D:spiderdocsmergesheet.py
全部代码
import wx
from openpyxl import load_workbook, Workbook
class MyApp(wx.App):
def OnInit(self):
frame = MyFrame(None, title="Excel Sheet Merger")
frame.Show()
return True
class MyFrame(wx.Frame):
def __init__(self, parent, title):
super(MyFrame, self).__init__(parent, title=title, size=(300, 200))
panel = wx.Panel(self)
vbox = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL)
self.button = wx.Button(panel, label="Select Excel File")
self.button.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, self.on_open_file)
vbox.Add(self.button, 0, wx.ALL | wx.CENTER, 5)
panel.SetSizer(vbox)
def on_open_file(self, event):
with wx.FileDialog(self, "Open Excel file", wildcard="Excel files (*.xlsx)|*.xlsx",
style=wx.FD_OPEN | wx.FD_FILE_MUST_EXIST) as fileDialog:
if fileDialog.ShowModal() == wx.ID_CANCEL:
return
path = fileDialog.GetPath()
self.merge_sheets(path)
def merge_sheets(self, filepath):
wb = load_workbook(filepath)
new_wb = Workbook()
new_ws = new_wb.active
new_ws.title = "Merged Sheet"
for i, sheet_name in enumerate(wb.sheetnames[:5]):
ws = wb[sheet_name]
for row in ws.iter_rows(values_only=True):
new_ws.append(row)
save_path = filepath.replace('.xlsx', '_merged.xlsx')
new_wb.save(save_path)
wx.MessageBox(f"Merged file saved as: {save_path}", "Info", wx.OK | wx.ICON_INFORMATION)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app = MyApp()
app.MainLoop()
环境准备
首先,确保你的环境中安装了pandas和openpyxl库。如果没有安装,可以通过以下命令安装:
pip install pandas openpyxl
代码分析
下面是一个简单的Python脚本,用于合并一个Excel文件中的前5个工作表:
import pandas as pd
def merge_sheets(file_path, output_file, num_sheets=5):
# 加载Excel文件
xls = pd.ExcelFile(file_path)
# 创建一个空的DataFrame用于存储合并后的数据
merged_df = pd.DataFrame()
# 循环读取前num_sheets个工作表
for sheet_name in xls.sheet_names[:num_sheets]:
# 读取每个工作表的数据
df = pd.read_excel(xls, sheet_name=sheet_name)
# 将读取的数据追加到merged_df中
merged_df = pd.concat([merged_df, df], ignore_index=True)
# 将合并后的数据保存到新的Excel文件
merged_df.to_excel(output_file, index=False)
# 调用函数
file_path = 'path_to_your_excel_file.xlsx'
output_file = 'merged_excel_file.xlsx'
merge_sheets(file_path, output_file)
代码解释
-
导入库:首先,我们导入了
pandas库,它是Python中用于数据处理和分析的强大工具。 -
定义函数:我们定义了一个名为
merge_sheets的函数,它接受三个参数:file_path(Excel文件的路径)、output_file(输出文件的名称)、num_sheets(需要合并的工作表数量,默认为5)。 -
加载Excel文件:使用
pd.ExcelFile函数加载Excel文件,这样我们可以访问文件中的所有工作表。 -
初始化DataFrame:创建一个空的
DataFrame,merged_df,用于存储合并后的数据。 -
循环读取工作表:通过
xls.sheet_names获取所有工作表的名称,并循环读取前num_sheets个工作表。对于每个工作表,使用pd.read_excel函数读取数据,并使用pd.concat函数将其追加到merged_df中。 -
保存合并后的数据:最后,使用
to_excel函数将合并后的数据保存到新的Excel文件中。
运行结果
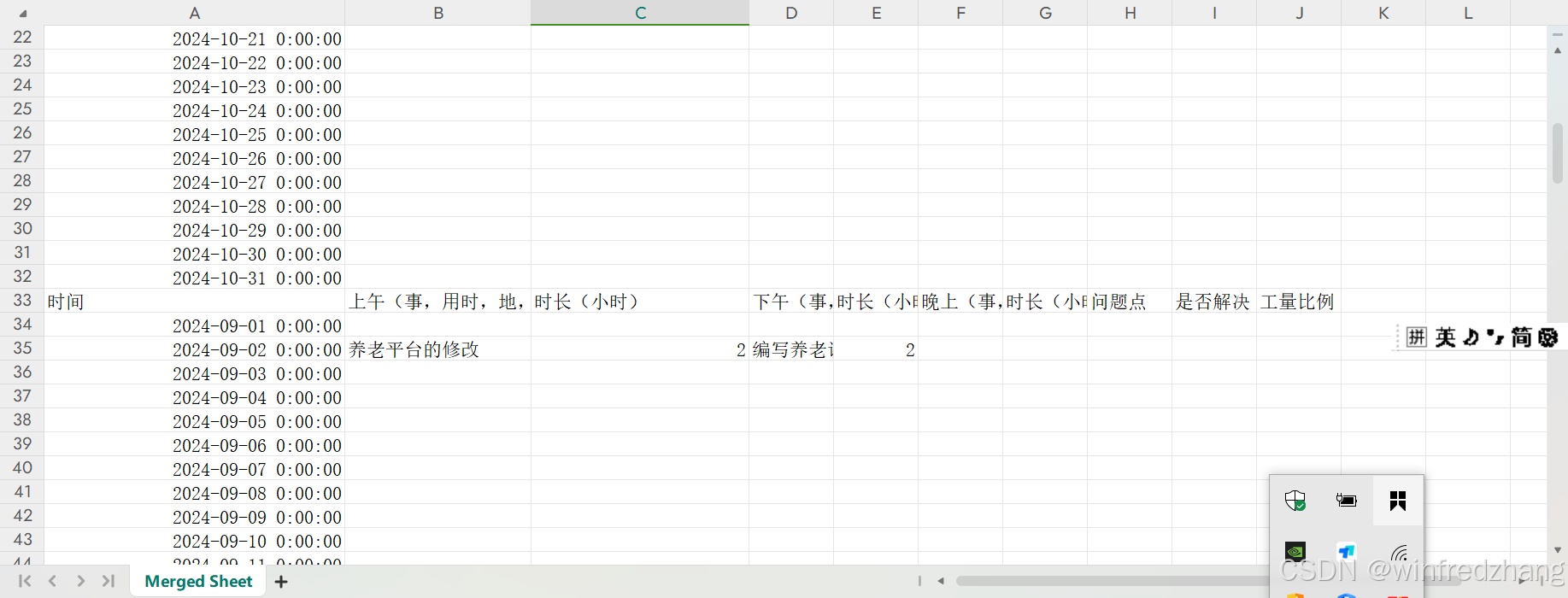
注意事项
- 确保
file_path和output_file正确指向了你的文件路径和期望的输出文件。 - 如果你的Excel文件中的工作表数量超过了5个,你可以通过修改
num_sheets参数来调整需要合并的工作表数量。 - 合并的数据将按照它们在原始文件中的顺序排列。
通过使用Python脚本自动化合并Excel工作表的过程,我们可以节省大量的时间和精力,特别是在处理大型数据集时。这种方法不仅提高了效率,而且减少了人为错误的可能性。
以上就是使用Python合并Excel文件中的多个Sheet的实现过程的详细内容,更多关于Python合并多个Sheet的资料请关注IT俱乐部其它相关文章!

