本篇博客使用python实现了一个简易的SSL,以帮助理解SSL的大致实现流程。
SSL(Secure Socket Layer)安全套接层是Netscape公司率先采用的网络安全协议。它是在传输通信协议(TCP/IP)上实现的一种安全协议,采用公开密钥技术。
运行环境
- 操作系统:浪潮云启操作系统 InLinux 23.12 LTS SP1
- python版本:3.9.9
- 使用的python包:cryptography、ownca、signify
浪潮云启操作系统(InLinux)面向企业级业务,提供自主可控、安全可靠的新一代服务器操作系统,全面支持云计算、大数据、人工智能、物联网等新型场景,具备性能高效、扩展便捷、管理智能、内生安全等特性。
运行前准备
# 安装python yum install -y python # 安装python包 pip install cryptography ownca signify
程序实现与流程说明
本程序实现了一个简易的SSL,共分为三个模块:CA.py,server.py,client.py。
CA.py负责签发证书,server.py与client.py通信,过程中会实现生成公私钥对、会话密钥等过程。为了简易性,server能够从本地直接获取证书,且只有server对client检查证书。
程序流程如下:
- CA生成根证书、公私钥对
- client生成公私钥对、向CA发送CSR请求
- CA收到CSR请求,用私钥签名,向client发送签名证书,client拿到证书
- client第一次向server发送数据,并附带证书信息
- server检验证书信息,并生成session_key,利用client公钥加密session_key,将密文发回给client,之后的对话用session_key验证。
- client解密session_key,利用消息和session_key生成MAC,向server发送消息并附带MAC
- server收到消息并验证MAC,对话结束。
运行截图
CA.py
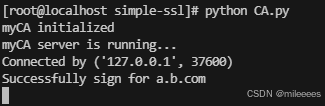
server.py
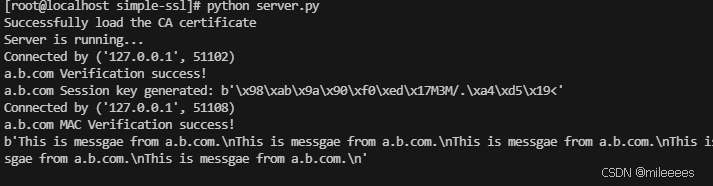
client.py
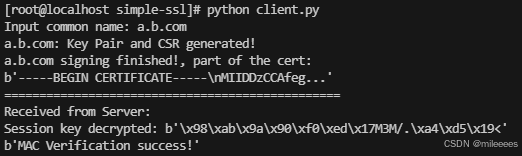
证书目录:
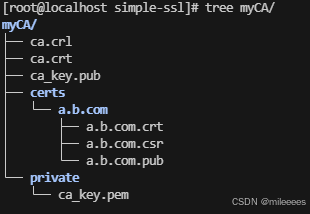
代码
CA.py
import ownca.ownca
import socket
from cryptography import x509
from cryptography.x509 import NameOID
ca = ownca.CertificateAuthority(ca_storage='./myCA',common_name='myCA')
print("myCA initialized")
HOST = "127.0.0.1" # Standard loopback interface address (localhost)
PORT = 11111 # Port to listen on (non-privileged ports are > 1023)
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
server_socket.bind((HOST, PORT))
server_socket.listen(5)
print("myCA server is running...")
while True:
conn, addr = server_socket.accept()
print(f"Connected by {addr}")
data = conn.recv(2048)
csr = x509.load_pem_x509_csr(data)
try:
# sign the CSR, if success, the certificate will generate and store
ca.sign_csr(csr,csr.public_key(),maximum_days=825)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
# extract CN from CSR
common_name = csr.subject.get_attributes_for_oid(NameOID.COMMON_NAME)[0].value
# load the issued certificate from existing file
load_cert = ca.load_certificate(common_name)
print('Successfully sign for ' + common_name)
# Send the certificate bytes
send_data = load_cert.cert_bytes
conn.sendall(send_data)
conn.close()
client.py
import socket
import pickle
from cryptography import x509
from cryptography.x509.oid import NameOID
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes, hmac
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import serialization
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import rsa, padding
def generateCSR(common_name, private_key):
csr = x509.CertificateSigningRequestBuilder().subject_name(x509.Name([
# Provide various details about who we are.
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.COUNTRY_NAME, u"CN"),
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.STATE_OR_PROVINCE_NAME, u"Beijing"),
# x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.LOCALITY_NAME, u"Richmond"),
# x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.ORGANIZATION_NAME, u"My Organization"),
x509.NameAttribute(NameOID.COMMON_NAME, common_name),
])).sign(private_key, hashes.SHA256())
return csr
def RSADecryption(cipher, private_key):
msg = private_key.decrypt(
cipher,
padding.OAEP(
mgf=padding.MGF1(algorithm=hashes.SHA256()),
algorithm=hashes.SHA256(),
label=None
)
)
return msg
# Generate the RSA private key
private_key = rsa.generate_private_key(public_exponent=65537, key_size=2048)
cn = input("Input common name: ")
csr = generateCSR(cn, private_key)
public_key = private_key.public_key()
# public_key = csr.public_key()
csr_bytes = csr.public_bytes(serialization.Encoding.PEM)
print(cn + ": Key Pair and CSR generated!")
HOST = "127.0.0.1" # The server's hostname or IP address
CA_PORT = 11111 # The CA server port
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
s.connect((HOST, CA_PORT))
s.sendall(csr_bytes) # send the generated CSR
cert_data = s.recv(2048)
print(cn + " signing finished!, part of the cert:")
print(cert_data[:40] + b'...')
print('================================================')
Server_PORT = 22222 # The Server port
session_key = b''
msg = b''
hMAC = b''
public_key_pem = public_key.public_bytes(
encoding=serialization.Encoding.PEM,
format=serialization.PublicFormat.SubjectPublicKeyInfo
)
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
s.connect((HOST, Server_PORT))
# send all params to the Server
params = [cn, cert_data, public_key_pem, session_key, msg, hMAC]
data = pickle.dumps(params)
s.sendall(data)
data = s.recv(2048)
print("Received from Server: ")
session_key = RSADecryption(data, private_key)
print("Session key decrypted:",session_key)
msg = b'This is messgae from ' + cn.encode('utf-8') + b'.n'
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
s.connect((HOST, Server_PORT))
msg = msg * 10
h = hmac.HMAC(session_key,hashes.SHA256())
h.update(msg)
hMAC = h.finalize()
# Send all params with valid session_key, msg and hMAC
params = [cn, cert_data, public_key_pem, session_key, msg, hMAC]
data = pickle.dumps(params)
s.sendall(data)
data = s.recv(2048)
print(data)
server.py
import os
import pickle
import socket
import ownca
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes, hmac
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.asymmetric import padding
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.serialization import load_pem_public_key
from signify.x509 import CertificateStore, VerificationContext, Certificate
ca = ownca.CertificateAuthority(ca_storage='./myCA',common_name='myCA')
print("Successfully load the CA certificate")
HOST = "127.0.0.1"
PORT = 22222
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
server_socket.bind((HOST, PORT))
server_socket.listen()
print("Server is running...")
# generate a list of random bytes as Session key
def generateSessionKey(byte_num=16):
return os.urandom(byte_num)
# Encrypt the msg using RSA
def RSAEncryption(msg, public_key):
cipher = public_key.encrypt(
msg,
padding.OAEP(
mgf=padding.MGF1(algorithm=hashes.SHA256()),
algorithm=hashes.SHA256(),
label=None
)
)
return cipher
while True:
conn, addr = server_socket.accept()
print(f"Connected by {addr}")
data = conn.recv(2048)
# find all params from the received data
params = pickle.loads(data)
cn = params[0]
cert_from_cli_pem = params[1]
public_key_pem = params[2] # for encrypting the session_key
session_key = params[3]
msg = params[4]
hMAC_to_check = params[5]
# if no session built
if not session_key:
try:
# Using Signify to verify the certificate
# Raise exception if verification error
trust_store = CertificateStore([Certificate.from_pem(ca.cert_bytes)], trusted=True)
context = VerificationContext(trust_store)
Certificate.from_pem(cert_from_cli_pem).verify(context)
except Exception as e:
print(cn + "Verification error: ", e)
conn.sendall(b"Verification error!n")
conn.close()
continue
finally:
print(cn + " Verification success!")
# load cert from stu_pem and find the public_key
public_key = load_pem_public_key(public_key_pem)
session_key = generateSessionKey()
print(cn + " Session key generated:",session_key)
cipher = RSAEncryption(session_key,public_key)
conn.sendall(cipher)
# valid session key
else:
h = hmac.HMAC(session_key, hashes.SHA256())
h.update(msg)
try:
h.verify(hMAC_to_check)
except Exception as e:
print(cn + " MAC Verification wrong:",e)
conn.close()
continue
finally:
print(cn + " MAC Verification success!")
print(msg)
conn.sendall(b'MAC Verification success!')
conn.close()
参考资料
到此这篇关于python实现简易SSL的项目实践的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关python实现简易SSL内容请搜索IT俱乐部以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持IT俱乐部!

