1.文件txt读写标准用法
1.1写入文件
要读取文件,首先得使用 open() 函数打开文件。
file = open(file_path, mode='r', encoding=None)
file_path:文件的路径,可以是绝对路径或者相对路径。
mode:文件打开模式,’r’ 代表以只读模式打开文件,这是默认值,‘w’表示写入模式。
encoding:文件的编码格式,像 ‘utf-8’、’gbk’ 等,默认值是 None。
下面写入文件的示例:
#写入文件,当open(file_name,'w')时清除文件内容写入新内容,当open(file_name,'a')时直接在文件结尾加入新内容
file_name = 'text.txt'
try:
with open(file_name,'w',encoding='utf-8') as file:
file.write("你好!我是老叶爱吃鱼")
file.write("n你好呀,老叶,很高兴认识你")
except Exception as e:
print(f'出错{e}')
系统会判断时候会有text.txt文件,没有的话会创建文件,加入写入内容,示例如下
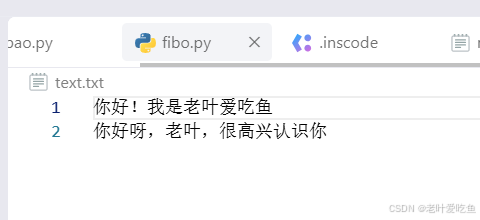
1.2读取文件
下面是读取文件示例:
#读取文件
try:
with open(file_name,'r',encoding='utf-8') as file:
print(file.read())
except Exception as e:
print(f'出错时输出{e}')
#打印出:你好!我是老叶爱吃鱼 你好呀,老叶,很高兴认识你
1.2.1 readline() 方法
readline() 方法每次读取文件的一行内容,返回一个字符串。
# 打开文件
file = open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
# 读取第一行
line = file.readline()
while line:
print(line.strip()) # strip() 方法用于去除行尾的换行符
line = file.readline()
# 关闭文件
file.close()
1.2.2 readlines() 方法
readlines() 方法会读取文件的所有行,并将每行内容作为一个元素存储在列表中返回。
# 打开文件
file = open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
# 读取所有行
lines = file.readlines()
for line in lines:
print(line.strip())
# 关闭文件
file.close()
1.2.3 迭代文件对象
可以直接对文件对象进行迭代,每次迭代会返回文件的一行内容。
# 打开文件
file = open('example.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
# 迭代文件对象
for line in file:
print(line.strip())
# 关闭文件
file.close()
2. 二进制文件读取
若要读取二进制文件,需将 mode 参数设置为 ‘rb’。
# 以二进制只读模式打开文件
with open('example.jpg', 'rb') as file:
# 读取文件全部内容
content = file.read()
# 可以对二进制数据进行处理,如保存到另一个文件
with open('copy.jpg', 'wb') as copy_file:
copy_file.write(content)
3. 大文件读取
对于大文件,不建议使用 read() 方法一次性读取全部内容,因为这可能会导致内存不足。可以采用逐行读取或者分块读取的方式。
3.1 逐行读取
# 逐行读取大文件
with open('large_file.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
for line in file:
# 处理每行内容
print(line.strip())
3.2 分块读取
# 分块读取大文件
chunk_size = 1024 # 每次读取 1024 字节
with open('large_file.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
while True:
chunk = file.read(chunk_size)
if not chunk:
break
# 处理每个数据块
print(chunk)
4.Excel表格文件的读写
4.1读取excel
import xlrd
import xlwt
from datetime import date,datetime
# 打开文件
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(r"D:python_filerequest_filesexcelfile.xlsx", formatting_info=False)
# 获取所有的sheet
print("所有的工作表:",workbook.sheet_names())
sheet1 = workbook.sheet_names()[0]
# 根据sheet索引或者名称获取sheet内容
sheet1 = workbook.sheet_by_index(0)
sheet1 = workbook.sheet_by_name("Sheet1")
# 打印出所有合并的单元格
print(sheet1.merged_cells)
for (row,row_range,col,col_range) in sheet1.merged_cells:
print(sheet1.cell_value(row,col))
# sheet1的名称、行数、列数
print("工作表名称:%s,行数:%d,列数:%d" % (sheet1.name, sheet1.nrows, sheet1.ncols))
# 获取整行和整列的值
row = sheet1.row_values(1)
col = sheet1.col_values(4)
print("第2行的值:%s" % row)
print("第5列的值:%s" % col)
# 获取单元格的内容
print("第一行第一列:%s" % sheet1.cell(0,0).value)
print("第一行第二列:%s" % sheet1.cell_value(0,1))
print("第一行第三列:%s" % sheet1.row(0)[2])
# 获取单元格内容的数据类型
# 类型 0 empty,1 string, 2 number, 3 date, 4 boolean, 5 error
print("第二行第三列的数据类型:%s" % sheet1.cell(3,2).ctype)
# 判断ctype类型是否等于data,如果等于,则用时间格式处理
if sheet1.cell(3,2).ctype == 3:
data_value = xlrd.xldate_as_tuple(sheet1.cell_value(3, 2),workbook.datemode)
print(data_value)
print(date(*data_value[:3]))
print(date(*data_value[:3]).strftime("%Y%m%d"))
4.2 设置单元格样式
style = xlwt.XFStyle() # 初始化样式 font = xlwt.Font() # 为样式创建字体 font.name = name # 设置字体名字对应系统内字体 font.bold = bold # 是否加粗 font.color_index = 5 # 设置字体颜色 font.height = height # 设置字体大小 # 设置边框的大小 borders = xlwt.Borders() borders.left = 6 borders.right = 6 borders.top = 6 borders.bottom = 6 style.font = font # 为样式设置字体 style.borders = borders return style
4.3写入excel
writeexcel = xlwt.Workbook() # 创建工作表 sheet1 = writeexcel.add_sheet(u"Sheet1", cell_overwrite_ok = True) # 创建sheet row0 = ["编号", "姓名", "性别", "年龄", "生日", "学历"] num = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] column0 = ["a1", "a2", "a3", "a4", "a5", "a6", "a7", "a8"] education = ["小学", "初中", "高中", "大学"] # 生成合并单元格 i,j = 1,0 while i
5.cvs文件的读写操作
5.1读取cvs文件
# 读取 CSV 文件
def read_from_csv(file_path):
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
print("读取到的 CSV 文件内容如下:")
for row in reader:
print(row)
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"错误: 文件 {file_path} 未找到!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"读取文件时出错: {e}")
5.2写入cvs文件
# 写入 CSV 文件
def write_to_csv(file_path, data):
try:
with open(file_path, 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as csvfile:
writer = csv.writer(csvfile)
# 写入表头
writer.writerow(['Name', 'Age', 'City'])
# 写入数据行
for row in data:
writer.writerow(row)
print(f"数据已成功写入 {file_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"写入文件时出错: {e}")
6.SQL文件读取
import sqlite3
import pandas as pd
# 连接到SQLite数据库
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
# 读取数据库表
query = "SELECT * FROM table_name"
data = pd.read_sql(query, conn)
print(data.head())
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
7.cvs、xls、txt文件相互转换
一般情况下python只会对cvs文件进行数据处理,那么对于很多文件属于二进制文件不能直接处理,那么需要将二进制转为cvs文件后才能处理,如xls是二进制文件需要对xls文件转为cvs文件,操作数据后再转成xls文件即可
7.1xls文件转cvs文件
import pandas as pd
def xls_to_csv(xls_file_path, csv_file_path):
try:
df = pd.read_excel(xls_file_path)
df.to_csv(csv_file_path, index=False)
print(f"成功将 {xls_file_path} 转换为 {csv_file_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换过程中出现错误: {e}")
# 示例调用
xls_file = 'example.xls'
csv_file = 'example.csv'
xls_to_csv(xls_file, csv_file)
7.2cvs文件转xls文件
import pandas as pd
def csv_to_xls(csv_file_path, xls_file_path):
try:
df = pd.read_csv(csv_file_path)
df.to_excel(xls_file_path, index=False)
print(f"成功将 {csv_file_path} 转换为 {xls_file_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换过程中出现错误: {e}")
# 示例调用
csv_file = 'example.csv'
xls_file = 'example.xls'
csv_to_xls(csv_file, xls_file)
7.3txt文件转cvs文件
import pandas as pd
def txt_to_csv(txt_file_path, csv_file_path):
try:
# 假设 txt 文件以空格分隔,根据实际情况修改 sep 参数
df = pd.read_csv(txt_file_path, sep=' ', header=None)
df.to_csv(csv_file_path, index=False, header=False)
print(f"成功将 {txt_file_path} 转换为 {csv_file_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换过程中出现错误: {e}")
# 示例调用
txt_file = 'example.txt'
csv_file = 'example.csv'
txt_to_csv(txt_file, csv_file)
7.4csv文件转txt文件
import pandas as pd
def csv_to_txt(csv_file_path, txt_file_path):
try:
df = pd.read_csv(csv_file_path)
df.to_csv(txt_file_path, sep=' ', index=False, header=False)
print(f"成功将 {csv_file_path} 转换为 {txt_file_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"转换过程中出现错误: {e}")
# 示例调用
csv_file = 'example.csv'
txt_file = 'example.txt'
csv_to_txt(csv_file, txt_file)
以上就是python中各种常见文件的读写操作与类型转换详细指南的详细内容,更多关于python文件读写与类型转换的资料请关注IT俱乐部其它相关文章!

